- Definition of Cyber Security
- Definition of Information Security
- Differences in Scope
- Differences in Focus
- Differences in Threats: What Is The Difference Between Cyber Security And Information Security
- Differences in Controls
- Differences in Responsibilities
- Differences in Technologies
- Differences in Standards and Regulations
- Provide examples of specific courses and certifications available in each field
- Differences in Career Paths
- Differences in Industry Applications
- Differences in Future Trends
- Conclusion
- FAQ Section
What is the difference between cyber security and information security – In the realm of digital protection, the distinction between cybersecurity and information security is a crucial one. Cybersecurity focuses on safeguarding digital assets, while information security encompasses a broader range of information, including both digital and physical assets. Understanding these differences is essential for effective security management.
Cybersecurity measures aim to protect computer systems, networks, and data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. Information security, on the other hand, encompasses the protection of all forms of information, regardless of its format or location, from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction.
Definition of Cyber Security
Cyber security is the practice of protecting computer systems, networks, and data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction.
It involves the implementation of security measures to prevent, detect, and respond to cyber threats, which can include malicious software, hacking, phishing, and denial-of-service attacks.
Scope and Objectives of Cyber Security
The scope of cyber security encompasses all aspects of computer systems and networks, including hardware, software, and data.
- Confidentiality:Protecting data from unauthorized access or disclosure.
- Integrity:Ensuring the accuracy and completeness of data.
- Availability:Ensuring that data and systems are accessible to authorized users when needed.
Definition of Information Security
Information security refers to the practice of protecting information from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction.
The scope of information security encompasses all types of information, including sensitive data, intellectual property, and personally identifiable information. Its objectives are to:
- Maintain the confidentiality of information, ensuring that it is only accessible to authorized individuals.
- Preserve the integrity of information, preventing unauthorized modification or deletion.
- Ensure the availability of information, making it accessible to authorized users when needed.
Real-World Examples of Information Security Breaches
Information security breaches can have significant consequences for individuals, organizations, and society.
- Identity theft:Unauthorized access to personal information, such as social security numbers or credit card details, can lead to identity theft.
- Financial loss:Data breaches can result in financial losses for organizations, including stolen funds, damaged reputation, and legal liability.
- National security breaches:Cyberattacks on government systems can compromise sensitive information and disrupt critical infrastructure.
Impact of Information Security Breaches
The impact of information security breaches can be far-reaching:
- Individuals:Breaches can cause financial loss, identity theft, and emotional distress.
- Organizations:Breaches can damage reputation, erode customer trust, and lead to legal and financial penalties.
- Society:Breaches can undermine public trust in technology and erode the integrity of critical infrastructure.
Differences in Scope
Cyber security and information security share a common goal of protecting information and systems from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. However, their scopes differ in terms of the assets they protect and the threats they address.
Cyber security focuses primarily on protecting computer systems, networks, and data from digital threats such as malware, hacking, and cyberattacks. It involves measures to protect against unauthorized access, data breaches, and system disruptions. Information security, on the other hand, encompasses a broader range of assets, including physical assets such as documents, records, and facilities.
It also addresses threats such as theft, loss, or unauthorized disclosure of information, regardless of the medium in which it is stored or transmitted.
Areas of Overlap and Distinction
- Overlap:Both cyber security and information security share the common goal of protecting information and systems from unauthorized access and misuse. They both involve measures to prevent, detect, and respond to security threats.
- Distinction:Cyber security focuses primarily on protecting digital assets and systems, while information security encompasses a broader range of assets, including physical assets and information in all forms.
Impact of Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies such as cloud computing, mobile devices, and the Internet of Things (IoT) are expanding the scope of both cyber security and information security. These technologies create new attack surfaces and increase the volume and complexity of security threats.
As a result, organizations need to adopt a comprehensive approach to security that addresses both cyber and information security risks.
Potential for Convergence or Divergence
In the future, cyber security and information security may converge or diverge depending on the evolution of technology and the threat landscape. If digital threats continue to dominate, cyber security may become increasingly specialized and distinct from information security. However, if physical threats remain significant or new threats emerge, information security may expand its scope to encompass both digital and physical security.
Differences in Focus
Cyber security and information security differ in their primary focus. Cyber security specifically targets the protection of digital assets, including computer networks, systems, and data. It primarily focuses on threats originating from the digital realm, such as cyber attacks, malware, and unauthorized access.
Information security, on the other hand, encompasses a broader range of information, including both digital and physical assets. It aims to protect all forms of information, regardless of its format or location. Information security addresses threats that can arise from both digital and non-digital sources, such as physical theft, data breaches, and natural disasters.
Threats and Vulnerabilities
- Cyber security: focuses on threats such as hacking, phishing, ransomware, and denial-of-service attacks.
- Information security: addresses threats such as data breaches, identity theft, unauthorized access, and physical theft of devices or documents.
Key Differences Table
| Aspect | Cyber Security | Information Security |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Digital assets | All forms of information |
| Threats | Cyber attacks, malware | Data breaches, physical theft |
| Scope | Digital realm | Both digital and physical realms |
Differences in Threats: What Is The Difference Between Cyber Security And Information Security
Cyber security and information security address distinct types of threats, although there is some overlap. Cyber security primarily focuses on threats that target computer systems, networks, and data, while information security encompasses a broader range of threats, including those that target physical assets, personnel, and processes.
Cyber security threats often involve unauthorized access, data breaches, malware attacks, and denial-of-service attacks. Information security threats can include physical theft or damage of assets, espionage, fraud, and social engineering attacks.
Cyber Security Threats
- Unauthorized access:Gaining access to a computer system or network without authorization, often through hacking or phishing.
- Data breaches:The unauthorized acquisition of sensitive or confidential information from a computer system or network.
- Malware attacks:The deployment of malicious software, such as viruses, worms, or Trojans, to damage or disrupt computer systems or networks.
- Denial-of-service attacks:Overwhelming a computer system or network with traffic, rendering it unavailable to legitimate users.
Information Security Threats
- Physical theft or damage of assets:The unauthorized removal or destruction of physical assets, such as computers, servers, or documents.
- Espionage:The unauthorized acquisition of sensitive or confidential information by unauthorized individuals or organizations.
- Fraud:The intentional deception or misrepresentation of information to obtain an unauthorized benefit.
- Social engineering attacks:The use of deception or manipulation to trick individuals into revealing sensitive or confidential information.
The nature of threats has evolved over time, with the increasing sophistication of cyber attacks and the growing interconnectedness of systems and networks. Emerging threats include ransomware attacks, which encrypt data and demand payment for its release, and supply chain attacks, which target vulnerabilities in software or hardware used by multiple organizations.
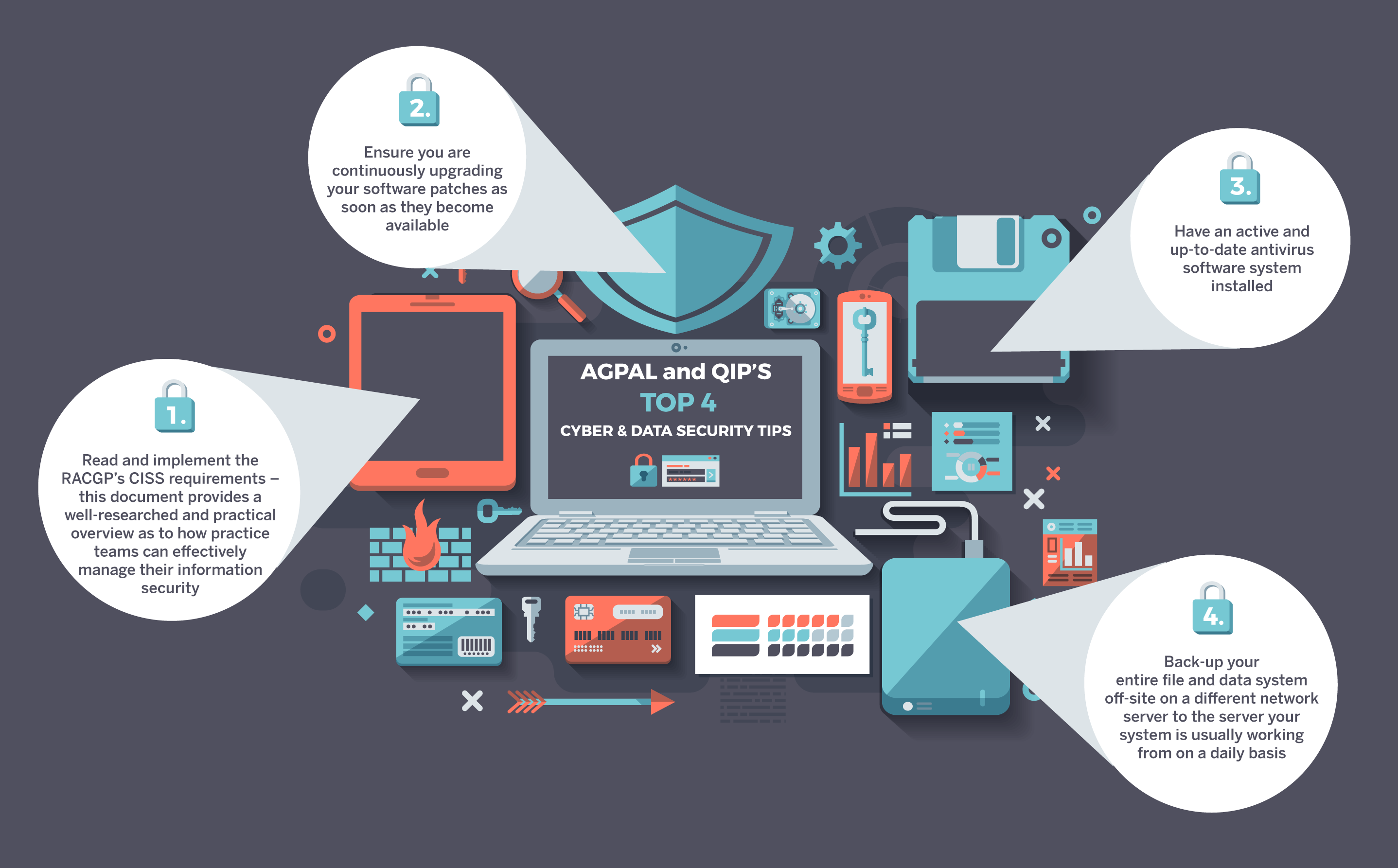
Differences in Controls
Cyber security and information security employ distinct controls to safeguard systems and data. These controls range from technical measures to administrative policies, each designed to address specific threats and vulnerabilities.
Cyber security controls focus on protecting against external threats, such as malware, hacking, and network intrusions. These controls include firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption technologies. Information security controls, on the other hand, are broader in scope and aim to protect data and systems from both internal and external threats.
They encompass measures such as access control, data classification, and disaster recovery plans.
Effectiveness of Controls
The effectiveness of controls depends on the nature of the threat and the specific context in which they are implemented. For instance, firewalls are highly effective in blocking unauthorized network access, while access control mechanisms can prevent unauthorized individuals from accessing sensitive data.
However, no single control is foolproof. Cybercriminals are constantly evolving their techniques, and organizations must continuously adapt their controls to stay ahead of these threats. A combination of different types of controls, layered in a comprehensive security architecture, provides the most robust protection against cyberattacks and information breaches.
Differences in Responsibilities
Professionals in cyber security and information security have distinct roles and responsibilities. Cyber security professionals focus on protecting computer systems and networks from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. They are responsible for implementing and maintaining security measures, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and anti-malware software.
They also monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and respond to security incidents.Information security professionals, on the other hand, are responsible for protecting the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information. They develop and implement policies and procedures to protect information from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction.
They also conduct risk assessments and audits to identify and mitigate security risks.The skill sets and expertise required for each field are also different. Cyber security professionals typically have a strong background in computer science and network security. They are familiar with operating systems, networking protocols, and security tools.
Information security professionals, on the other hand, typically have a background in information management, risk management, and compliance. They are familiar with information security regulations and standards, and they have experience in developing and implementing security policies and procedures.
Roles and Responsibilities of Cyber Security Professionals
* Implement and maintain security measures
- Monitor network traffic for suspicious activity
- Respond to security incidents
- Investigate and remediate security breaches
- Provide security training and awareness to employees
Roles and Responsibilities of Information Security Professionals
* Develop and implement security policies and procedures
- Conduct risk assessments and audits
- Manage security incident response
- Ensure compliance with security regulations and standards
- Provide security training and awareness to employees
Differences in Technologies
Cyber security and information security utilize various technologies to protect against cyber threats. These technologies differ in their capabilities, advantages, and disadvantages.
- Cyber Security Technologies
Cyber security technologies focus on protecting networks, systems, and data from unauthorized access, disruption, or theft. Some common technologies include:
- Firewalls
- Intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS)
- Virtual private networks (VPNs)
- Multi-factor authentication
- Anti-malware software
- Information Security Technologies
Information security technologies aim to protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information. These technologies include:
- Data encryption
- Access control
- Data backup and recovery
- Information rights management (IRM)
- Security information and event management (SIEM)
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Technologies
The choice of technology depends on the specific threats being addressed. For example, firewalls are effective in preventing unauthorized access to networks, while encryption protects data from unauthorized disclosure. However, no single technology can provide complete protection against all threats.
Differences in Standards and Regulations

Cyber security and information security are governed by distinct standards and regulations that shape their implementation and enforcement. These standards and regulations provide guidelines, best practices, and compliance requirements to ensure the protection of sensitive data and systems.
Cyber security, unlike information security, focuses on the protection of digital assets and data in cyberspace, while information security safeguards all forms of data, whether physical or digital. This distinction is highlighted in the context of troubleshooting a common issue encountered with the Samsung Easy Printer Manager Wi-Fi Wizard.
If the wizard is not working, it is recommended to consult this guide for potential solutions. Nevertheless, understanding the difference between cyber security and information security is crucial for effective data protection strategies.
Cyber Security Standards and Regulations
Cyber security standards and regulations focus on protecting systems, networks, and data from cyber threats and attacks. Notable examples include:
- ISO 27001/27002: International standards for information security management systems
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework: US-based framework for managing cybersecurity risks
- PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard): Standard for protecting payment card data
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act): US regulation protecting patient health information
Information Security Standards and Regulations
Information security standards and regulations focus on protecting the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information, regardless of its location or format. Examples include:
- ISO 15408: International standard for information security management
- COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies): Framework for IT governance and control
- Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX): US regulation requiring financial reporting and internal control
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): EU regulation protecting personal data
The impact of these standards and regulations on the implementation of security measures is significant. They provide organizations with a structured approach to identifying, assessing, and mitigating security risks. Compliance with these standards and regulations is often mandatory for organizations operating in regulated industries or handling sensitive data.
Provide examples of specific courses and certifications available in each field
Cyber security and information security are two closely related but distinct fields. Both fields are concerned with protecting information from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. However, there are some key differences between the two fields.
One of the most significant differences between cyber security and information security is the scope of the field. Cyber security focuses on protecting information systems from cyber threats, such as malware, hackers, and phishing attacks. Information security, on the other hand, focuses on protecting information from all threats, including physical threats, such as theft or natural disasters.
Cyber Security Courses and Certifications
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP)
- Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH)
- Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA)
- Master of Science in Cyber Security
- Bachelor of Science in Cyber Security
Information Security Courses and Certifications
- Certified Information Security Manager (CISM)
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP)
- Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA)
- Master of Science in Information Security
- Bachelor of Science in Information Security
The duration and cost of these programs vary depending on the institution and the level of certification. However, most programs can be completed in one to two years. The cost of the programs can range from a few thousand dollars to tens of thousands of dollars.
There are several advantages to obtaining a certification in cyber security or information security. Certifications can demonstrate your knowledge and skills to potential employers and can help you advance your career. Certifications can also help you stay up-to-date on the latest trends in cyber security and information security.
There are also some disadvantages to obtaining a certification in cyber security or information security. Certifications can be expensive and time-consuming to obtain. Additionally, certifications may not be required for all jobs in the field.
Professional development is essential for anyone working in the field of cyber security or information security. The field is constantly evolving, and new threats are emerging all the time. It is important to stay up-to-date on the latest trends in order to protect your organization from cyber threats.
There are several ways to obtain professional development in the field of cyber security or information security. You can attend conferences and workshops, read books and articles, and take online courses. You can also join professional organizations, such as the Information Systems Security Association (ISSA) or the Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP).
The following table compares the curriculum and certification requirements for cyber security and information security professionals.
| Cyber Security | Information Security | |
|---|---|---|
| Curriculum | Network security, cryptography, malware analysis, ethical hacking, risk management | Information security management, risk management, compliance, audit, security controls |
| Certification requirements | CISSP, CEH, CISA | CISM, CISSP, CISA |
Real-world examples
In 2017, the Equifax data breach exposed the personal information of over 145 million Americans. The breach was caused by a vulnerability in the company’s website that allowed hackers to access the company’s database. This breach is an example of a cyber security failure.
In 2018, the Marriott data breach exposed the personal information of over 500 million guests. The breach was caused by a malware attack that allowed hackers to access the company’s reservation system. This breach is an example of an information security failure.
Differences in Career Paths
Career paths in cyber security and information security offer a wide range of opportunities for professionals with varying skills and interests.
Cyber Security
Cyber security professionals focus on protecting computer systems, networks, and data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. Career paths in cyber security include:
- Cyber Security Analyst
- Security Engineer
- Network Security Specialist
- Information Security Analyst
- Cyber Security Manager
With experience and specialization, cyber security professionals can advance to roles such as:
- Chief Information Security Officer (CISO)
- Cyber Security Architect
- Cyber Threat Intelligence Analyst
- Penetration Tester
Information Security
Information security professionals focus on protecting the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information assets, including data, applications, and systems. Career paths in information security include:
- Information Security Analyst
- Security Engineer
- Network Security Specialist
- Data Security Analyst
- Information Security Manager
With experience and specialization, information security professionals can advance to roles such as:
- Chief Information Security Officer (CISO)
- Information Security Architect
- Security Auditor
- Compliance Manager
Both cyber security and information security offer ample opportunities for career growth and specialization. The specific career path one takes will depend on their interests, skills, and experience.
Differences in Industry Applications
Cyber security and information security are applied in different ways across various industries. The specific challenges and best practices for implementing security measures vary depending on the industry’s unique requirements and risk profile.
Finance
The finance industry is heavily reliant on the secure handling of sensitive financial data, such as customer account information and transaction details. Cyber security measures are crucial to protect against unauthorized access, data breaches, and financial fraud. Strong encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular security audits are essential.
Healthcare
The healthcare industry deals with highly sensitive patient data, making it a prime target for cyberattacks. Information security measures are vital to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of patient records. Compliance with industry regulations, such as HIPAA, is paramount.
Robust access controls, data encryption, and incident response plans are critical.
Government
Government agencies possess vast amounts of sensitive information, including national security secrets and citizen data. Cyber security is essential to protect against espionage, cyber warfare, and data breaches. Advanced threat detection systems, secure communication channels, and robust encryption are necessary.
Manufacturing
The manufacturing industry faces unique cyber security challenges due to the increasing use of interconnected systems and industrial control systems. Information security measures are crucial to protect against operational disruptions, data theft, and sabotage. Physical security measures, network segmentation, and vulnerability management are essential.
Retail
The retail industry handles large volumes of customer data and financial transactions. Cyber security measures are vital to protect against data breaches, payment fraud, and reputational damage. Secure payment gateways, fraud detection systems, and customer data protection are essential.
Table: Key Differences in Cyber Security and Information Security Applications Across Industries
| Industry | Cyber Security Focus | Information Security Focus ||—|—|—|| Finance | Data protection, fraud prevention | Regulatory compliance, data governance || Healthcare | Patient data privacy, medical device security | HIPAA compliance, data integrity || Government | National security, espionage prevention | Data classification, access controls || Manufacturing | Operational resilience, industrial control system security | Data protection, network security || Retail | Customer data protection, payment security | Fraud prevention, data privacy |
Real-World Case Studies
* Finance:The 2014 Target data breach compromised the personal information of millions of customers, highlighting the importance of robust cyber security measures in the finance industry.
Healthcare
The 2017 WannaCry ransomware attack crippled hospital systems worldwide, emphasizing the need for strong information security measures in healthcare.
Government
The 2015 Office of Personnel Management (OPM) data breach exposed the personal information of millions of federal employees, demonstrating the critical role of cyber security in protecting sensitive government data.
Common Pitfalls and Lessons Learned
* Lack of employee training:Employees often pose a significant security risk due to phishing attacks and social engineering. Regular security awareness training is essential.
Insufficient patch management
Unpatched systems are vulnerable to known exploits. Regular patching and vulnerability management are crucial.
Weak access controls
Cyber security and information security are two closely related fields that both deal with the protection of information. However, there are some key differences between the two. Cyber security focuses on protecting information from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction.
Information security, on the other hand, focuses on protecting the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information. In other words, cyber security is concerned with protecting information from external threats, while information security is concerned with protecting information from both internal and external threats.
For example, cyber security would be responsible for protecting the network from unauthorized access, while information security would be responsible for protecting the data on the network from unauthorized access, modification, or destruction. One can easily manage print jobs, check toner levels, and troubleshoot issues using a tool like easy printer manager samsung xpress m2020w.
Both cyber security and information security are important aspects of protecting information, and organizations should take steps to implement both types of security measures.
Inadequate access controls can lead to unauthorized access and data breaches. Strong authentication mechanisms and role-based access control are necessary.
Differences in Future Trends

The future of cyber security and information security is constantly evolving, driven by the rapid pace of technological advancement and the increasing sophistication of cyber threats. Emerging trends in these fields are shaping the future of security practices and influencing the strategies organizations adopt to protect their data and systems.
One of the most significant trends in both cyber security and information security is the rise of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). These technologies are being used to automate security tasks, detect and respond to threats in real-time, and improve the overall efficiency of security operations.
AI and ML are also being used to develop new security tools and technologies, such as predictive analytics and threat intelligence platforms.
Convergence of Cyber Security and Information Security
Another emerging trend is the convergence of cyber security and information security. Traditionally, these two disciplines have been treated separately, but the increasing interconnectedness of systems and data is blurring the lines between them. As a result, organizations are increasingly adopting a more holistic approach to security that integrates cyber security and information security strategies.
Increased Focus on Data Privacy
The growing importance of data privacy is also driving changes in security practices. With the increasing amount of personal and sensitive data being collected and stored by organizations, there is a growing need for strong data privacy measures. This includes implementing robust data protection technologies, such as encryption and access controls, as well as developing policies and procedures to govern the collection, use, and disclosure of personal data.
Cloud Security, What is the difference between cyber security and information security
The adoption of cloud computing is another major trend that is impacting security practices. Cloud computing offers many benefits, such as increased flexibility, scalability, and cost savings. However, it also introduces new security challenges, such as the need to protect data and systems in a shared environment.
Organizations are increasingly investing in cloud security solutions, such as cloud access security brokers (CASBs) and cloud security posture management (CSPM) tools, to address these challenges.
Cybersecurity Mesh Architecture
Cybersecurity mesh architecture is a relatively new approach to network security that is gaining popularity. It involves distributing the security functions across multiple devices and locations, rather than relying on a centralized security infrastructure. This makes it more difficult for attackers to compromise the network and gain access to sensitive data.
Zero Trust
Zero trust is a security model that assumes that all users and devices are potential threats. This model requires all users to be authenticated and authorized before they are granted access to any resources. Zero trust is becoming increasingly popular as organizations adopt a more proactive approach to security.
Conclusion
Cyber security and information security are two distinct but interconnected fields that play a vital role in protecting organizations from various threats. Understanding the key differences between these two disciplines is crucial for effective security management and implementation.
The following table summarizes the key characteristics of cyber security and information security:
| Characteristic | Cyber Security | Information Security |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Focuses on protecting digital assets and systems from cyber threats | Focuses on protecting all types of information, regardless of its format or location |
| Focus | Protecting against unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction of digital assets | Protecting the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information |
| Threats | Cyberattacks, malware, hacking, phishing, social engineering | Data breaches, unauthorized access, information leakage, insider threats |
| Controls | Firewalls, intrusion detection systems, antivirus software, access control | Encryption, data backup, physical security, access control |
| Responsibilities | Chief Information Security Officer (CISO), IT security team | Information security officers, records managers, compliance officers |
| Technologies | Cybersecurity tools, threat intelligence, cloud security | Data protection software, encryption, identity management |
| Standards and Regulations | ISO 27001, NIST Cybersecurity Framework, PCI DSS | ISO 27001, HIPAA, GDPR |
Best Practices
- Conduct regular security risk assessments
- Implement a comprehensive security policy
- Educate employees on security best practices
- Use strong encryption and authentication measures
- Implement a data backup and recovery plan
- Monitor and respond to security incidents promptly
Key Takeaways
- Cyber security and information security are distinct but interconnected disciplines.
- Cyber security focuses on protecting digital assets from cyber threats, while information security focuses on protecting all types of information.
- Understanding the differences between these two fields is crucial for effective security management.
- Implementing a comprehensive security strategy that addresses both cyber security and information security is essential for protecting organizations from various threats.
FAQ Section
What is the primary difference between cybersecurity and information security?
Cybersecurity focuses on protecting digital assets, while information security encompasses a broader range of information, including both digital and physical assets.
What are the key objectives of cybersecurity?
To protect computer systems, networks, and data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction.
What are the key objectives of information security?
To protect all forms of information, regardless of its format or location, from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction.
Why is it important to understand the differences between cybersecurity and information security?
To implement effective security measures and ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information assets.