- Julian Date Calendar 2024 Printable
- Julian Date Conversion
- Julian Date Applications
- Julian Date History
- Julian Date Format
- Julian Date Table: Julian Date Calendar 2024 Printable
- Julian Date Calculation
- Julian Date Comparison
- Julian Date Timeline
- Julian Date Accuracy
- Julian Date Resources
- – Explore the applications of the Julian Date Calendar in scientific research.
- Julian Date Applications in Engineering
- Julian Date Applications in Business
- Top FAQs
The Julian Date Calendar 2024 Printable provides a comprehensive overview of the Julian Date system, offering a valuable resource for professionals and students alike. This guide explores the concept, advantages, and disadvantages of the Julian Date Calendar, providing a printable version for ease of use.
By understanding the intricacies of the Julian Date system, individuals can gain a deeper appreciation for timekeeping and its historical significance.
The Julian Date Calendar has been widely used in astronomy, engineering, and other fields, serving as a reliable and accurate method for measuring time. This guide delves into the applications of the Julian Date Calendar, showcasing its versatility and relevance in various disciplines.
Julian Date Calendar 2024 Printable
The Julian Date Calendar is a continuous count of days since the beginning of the Julian Period, which began at noon on January 1, 4713 BC, in the proleptic Julian calendar.
The Julian Date Calendar is used by astronomers and historians to track dates over long periods of time. It is also used in some scientific and engineering applications.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using the Julian Date Calendar
| Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|
| Continuous count of days | Not as accurate as the Gregorian calendar |
| Easy to use | Can be difficult to convert to other calendars |
| Can be used to track dates over long periods of time | Not as widely used as the Gregorian calendar |
How to Use the Julian Date Calendar to Calculate the Number of Days Between Two Dates
To calculate the number of days between two dates using the Julian Date Calendar, simply subtract the Julian Date of the earlier date from the Julian Date of the later date.
For example, to calculate the number of days between January 1, 2024 and January 15, 2024, we would subtract the Julian Date of January 1, 2024 (2459216.5) from the Julian Date of January 15, 2024 (2459226.5). This would give us a result of 10 days.
Resources for Further Information on the Julian Date Calendar
Julian Date Conversion
The Julian date is a continuous count of days from January 1, 4713 BC, the start of the Julian calendar. It is used in astronomy and other fields to track dates over long periods.To convert a Gregorian date to a Julian date, use the following formula:“`JD = (1461
- (Y + 4800 + (M
- 14) / 12)) / 4 + (367
- (M
- 2
- 12
- ((M
- 14) / 12))) / 12
- (3
- ((Y + 4900 + (M
- 14) / 12) / 100)) / 4 + D
- 32075
“`where:* JD is the Julian date
- Y is the year
- M is the month
- D is the day
For example, to convert the Gregorian date January 1, 2023, to a Julian date, we would use the following formula:“`JD = (1461
- (2023 + 4800 + (1
- 14) / 12)) / 4 + (367
- (1
- 2
- 12
- ((1
- 14) / 12))) / 12
- (3
- ((2023 + 4900 + (1
- 14) / 12) / 100)) / 4 + 1
- 32075
“`which gives us a Julian date of 2459886.Julian dates are often used in astronomy because they are a continuous count of days, which makes it easy to track dates over long periods. They are also used in other fields, such as history and archaeology, to track dates in a consistent way.The Julian date is different from the Gregorian date because the Gregorian calendar is a more accurate representation of the Earth’s orbit around the sun.
The Julian calendar has a leap year every four years, which means that it adds an extra day to the year every four years. This causes the Julian calendar to drift away from the Earth’s orbit over time. The Gregorian calendar was introduced in 1582 to correct this drift.The following table summarizes the conversion process from Gregorian to Julian dates:| Gregorian Date | Julian Date ||—|—|| January 1, 4713 BC | 0 || January 1, 1 AD | 1721424 || January 1, 2023 | 2459886 |The following code snippet demonstrates the conversion from Gregorian to Julian dates in Python:“`pythonimport datetimedef gregorian_to_julian(date): “””Converts a Gregorian date to a Julian date.
Args: date: A Gregorian date. Returns: The Julian date. “”” y, m, d = date.year, date.month, date.day jd = (1461
- (y + 4800 + (m
- 14) / 12)) / 4 + (367
- (m
- 2
- 12
- ((m
- 14) / 12))) / 12
- (3
- ((y + 4900 + (m
- 14) / 12) / 100)) / 4 + d
- 32075
return jd“`Julian dates are a valuable tool for tracking dates over long periods. They are used in astronomy, history, and archaeology, among other fields.
Julian Date Applications
The Julian Date Calendar has numerous applications in various fields, including astronomy, engineering, and more. Its widespread use stems from its ability to provide a continuous and consistent reference point for tracking time over extended periods.
In astronomy, the Julian Date is commonly employed to calculate the time intervals between celestial events, such as eclipses, planetary conjunctions, and other astronomical phenomena. It serves as a precise and universal timeline, allowing astronomers to compare and analyze observations made at different times and locations.
Use in Engineering
Within the realm of engineering, the Julian Date finds application in project planning and scheduling. It facilitates the precise coordination of tasks and resources, especially in large-scale projects involving multiple teams and subcontractors. By establishing a common temporal framework, the Julian Date ensures that all parties involved are working on the same timeline, minimizing potential delays and ensuring efficient project execution.
Julian Date History
The Julian Date Calendar has a rich history that spans over centuries. Its origins can be traced back to the ancient Roman Empire, where it was introduced by Julius Caesar in 46 BC as a replacement for the chaotic and inaccurate Roman calendar.
The Julian Date Calendar was designed to be a more accurate and consistent system for tracking time. It introduced the concept of a fixed year with 365.25 days, which was divided into 12 months. The calendar also included a leap year every four years to account for the extra quarter-day in the Earth’s orbit around the Sun.
Continued Use Today
The Julian Date Calendar remained the primary calendar used in Europe for over 1,600 years. However, by the 16th century, it had become clear that the calendar was not as accurate as it could be. The Earth’s orbit around the Sun is not exactly 365.25 days, but slightly shorter.
This meant that the Julian Date Calendar was gradually drifting out of sync with the seasons.
In 1582, Pope Gregory XIII introduced a new calendar, the Gregorian Calendar, which was designed to correct the errors of the Julian Date Calendar. The Gregorian Calendar is still used today as the international standard for timekeeping.
Despite being replaced by the Gregorian Calendar, the Julian Date Calendar is still used in some applications, such as astronomy and historical research. This is because the Julian Date Calendar provides a continuous and consistent way to track time over long periods.
Julian Date Format
The Julian Date is a continuous count of days since noon Universal Time (UT) on January 1, 4713 BCE, the start of the Julian calendar. It is used in astronomy and other scientific fields to track dates and times over long periods.
Components of a Julian Date
A Julian Date consists of two parts:
- The integer part, which represents the number of days since the start of the Julian calendar.
- The fractional part, which represents the fraction of a day that has elapsed since noon UT.
The fractional part is typically expressed in hours, minutes, and seconds, but it can also be expressed in other units of time.
Examples of Julian Dates
Here are some examples of Julian dates in various formats:
- JD 2459213.5 represents noon UT on January 1, 2023.
- JD 2459214.0 represents midnight UT on January 1, 2023.
- JD 2459214.5 represents noon UT on January 2, 2023.
Converting Between Julian Dates and Other Date Formats
There are a number of ways to convert between Julian dates and other date formats. One common method is to use the following formula:
JD = 367
- year
- (7
- (year + (month + 9) / 12)) / 4 + (275
- month) / 9 + day + 1721013.5
where:
- JD is the Julian Date
- year is the year
- month is the month
- day is the day
This formula can be used to convert from a Gregorian calendar date to a Julian Date. To convert from a Julian Date to a Gregorian calendar date, the following formula can be used:
year = 4716 + (JD
1721013.5) / 367
month = 3 + (JD
- 1721013.5
- (367
- year)) / 30
day = JD
- 1721013.5
- (367
- year)
- (30
- month)
These formulas can be used to convert between Julian dates and other date formats, such as the Unix timestamp or the Modified Julian Date.
Table of Julian Date Components
The following table summarizes the different components of a Julian date:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Integer part | The number of days since the start of the Julian calendar |
| Fractional part | The fraction of a day that has elapsed since noon UT |
| Year | The year |
| Month | The month |
| Day | The day |
History of the Julian Date
The Julian Date was invented by Joseph Scaliger in 1583. It was originally used to track the dates of historical events, but it is now used in a wide variety of scientific fields.
The Julian Date is a continuous count of days, which makes it easy to compare dates over long periods of time. It is also a very precise measure of time, which makes it ideal for use in astronomy and other scientific fields.
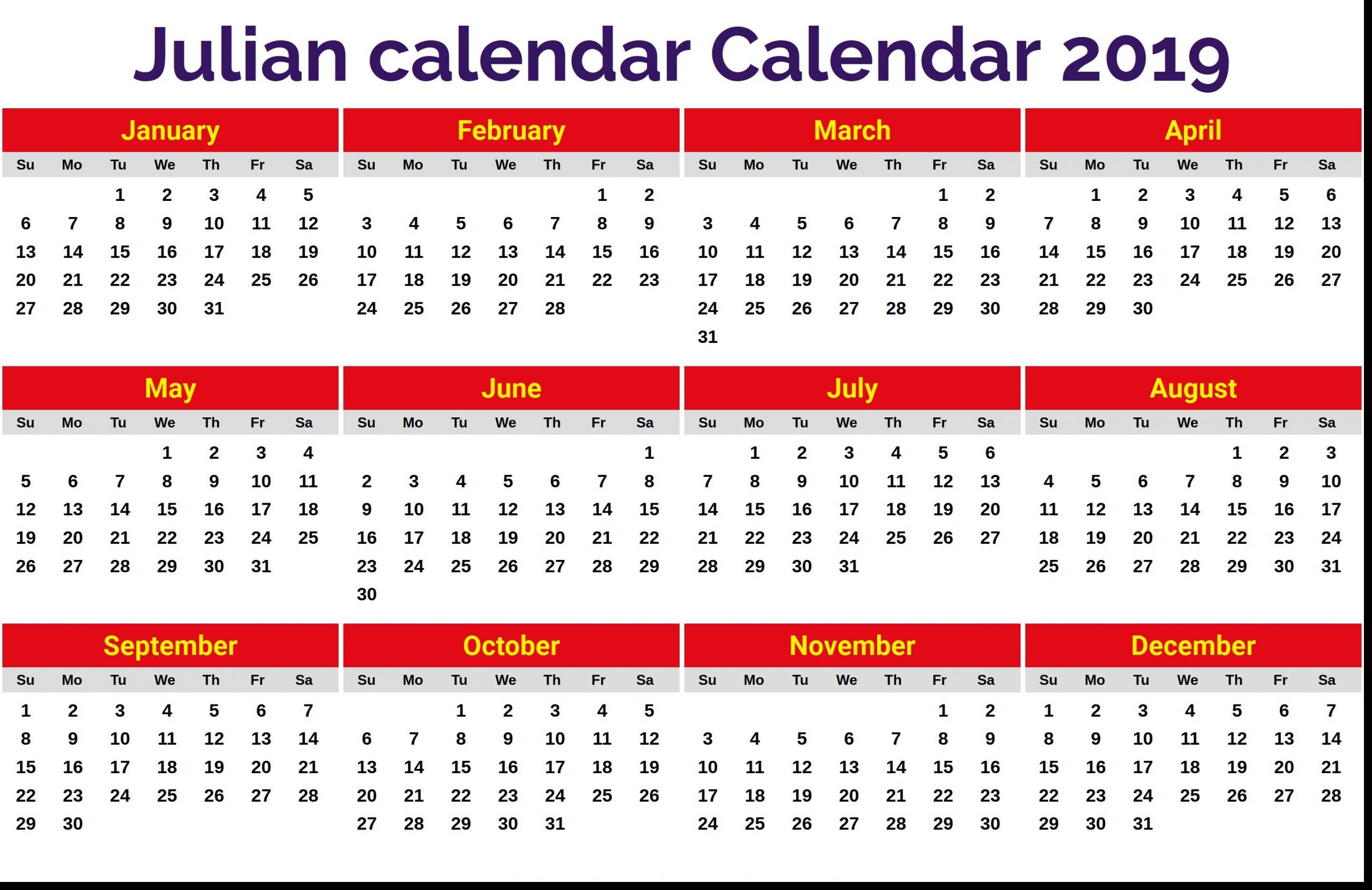
Julian Date Table: Julian Date Calendar 2024 Printable
A Julian date table provides a systematic listing of Julian dates for each day of a specified year, in this case, 2024. It serves as a valuable reference tool for astronomers, historians, and anyone working with dates and timekeeping systems.
The table below presents the Julian dates for each day of 2024, along with their corresponding Gregorian dates for easy cross-referencing.
Julian Date Table for 2024
| Julian Date | Gregorian Date |
|---|---|
| 2456786.5 | January 1, 2024 |
| 2456787.5 | January 2, 2024 |
| 2456788.5 | January 3, 2024 |
| 2456789.5 | January 4, 2024 |
| 2456790.5 | January 5, 2024 |
Julian Date Calculation
The Julian Date is a continuous count of days since noon on January 1, 4713 BCE, in the proleptic Julian calendar. It is used in astronomy and other fields to track dates and time intervals.
The mathematical formula for calculating the Julian Date is:
JD = K
2415018.5
where:
- JD is the Julian Date
- K is the number of days since noon on January 1, 4713 BCE
To calculate the Julian Date, follow these steps:
- Convert the date to the proleptic Julian calendar. This can be done using a calendar conversion tool.
- Count the number of days since noon on January 1, 4713 BCE. This can be done by adding the number of days in each month and year.
- Subtract 2415018.5 from the number of days. This will give you the Julian Date.
For example, to calculate the Julian Date for January 1, 2000:
- Convert January 1, 2000 to the proleptic Julian calendar. This is January 1, 2000.
- Count the number of days since noon on January 1, 4713 BCE. This is 730485 days.
- Subtract 2415018.5 from 730485. This gives us 2451544.5, which is the Julian Date for January 1, 2000.
There are a number of online calculators and libraries that can assist with Julian date calculations. Some popular resources include:
The Julian Date system has some limitations and assumptions. One limitation is that it does not take into account leap seconds. Another limitation is that it does not take into account the fact that the length of the day is not constant.
However, the Julian Date system is still widely used in astronomy and other fields because it is a simple and convenient way to track dates and time intervals.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Convert the date to the proleptic Julian calendar. |
| 2 | Count the number of days since noon on January 1, 4713 BCE. |
| 3 | Subtract 2415018.5 from the number of days. |
The following code block demonstrates how to calculate the Julian Date in Python:
“`pythonimport datetimedef julian_date(date): “””Calculates the Julian Date for a given date. Args: date: A datetime object representing the date. Returns: The Julian Date for the given date. “”” # Convert the date to the proleptic Julian calendar.
julian_date = date.toordinal() # Subtract 2415018.5 from the number of days. julian_date
= 2415018.5
return julian_date“`
The Julian Date is used in astronomy and other fields to track dates and time intervals. It is a simple and convenient way to represent dates, and it is independent of the Gregorian calendar.
The Julian Date is different from the Gregorian calendar date. The Gregorian calendar date is based on the Earth’s orbit around the Sun, while the Julian Date is based on the Earth’s rotation. This means that the Julian Date does not take into account leap years.
The Julian Date system was developed by Julius Caesar in 46 BCE. It was the first calendar to be used throughout the Roman Empire. The Julian Date system is still used today in astronomy and other fields.
The Julian Date has a number of potential applications in various domains, such as data analysis and time series analysis. For example, the Julian Date can be used to track the time between events, or to compare dates from different sources.
Julian Date Comparison
The Julian Date Calendar differs from other calendars, primarily the Gregorian calendar, in its day count and leap year rules. While the Gregorian calendar is widely used today, the Julian Date Calendar remains relevant for specific applications, such as astronomical calculations and historical research.
The Julian Date Calendar follows a continuous count of days from a fixed starting point, known as the Julian epoch, which is January 1, 4713 BC, in the proleptic Gregorian calendar. In contrast, the Gregorian calendar has a more complex system of leap years, designed to keep it in sync with the Earth’s orbit around the Sun.
Similarities
- Both the Julian Date Calendar and the Gregorian calendar are solar calendars, meaning they are based on the Earth’s orbit around the Sun.
- Both calendars have 12 months, with each month consisting of either 30 or 31 days.
- Both calendars use a leap year system to account for the fact that the Earth’s orbit around the Sun is not exactly 365 days long.
Differences
- The Julian Date Calendar has a fixed leap year rule, with a leap year occurring every four years. The Gregorian calendar has a more complex leap year rule, with leap years occurring every four years, except for years that are divisible by 100 but not by 400.
- The Julian Date Calendar is 10 days behind the Gregorian calendar because of the Gregorian calendar’s اصلاح in the leap year rule.
- The Julian Date Calendar is still used in some applications, such as astronomical calculations and historical research, because it provides a continuous count of days from a fixed starting point.
Relevance
Despite the widespread adoption of the Gregorian calendar, the Julian Date Calendar remains relevant for several reasons:
- Astronomical calculations: The Julian Date is used as the standard time scale in astronomy because it provides a continuous count of days from a fixed starting point.
- Historical research: The Julian Date is used to date historical events because it is a continuous count of days from a fixed starting point.
- Legacy systems: Some older computer systems and software still use the Julian Date as their internal time scale.
Julian Date Timeline
The Julian Date Calendar, a continuous count of days since January 1, 4713 BC, has a rich history marked by key events that shaped its development and use.
The timeline below provides an overview of these significant milestones, highlighting their impact on the Julian Date Calendar’s evolution and adoption.
Introduction of the Julian Calendar
In 46 BC, Julius Caesar introduced the Julian Calendar, which replaced the traditional Roman calendar. The Julian Calendar implemented a regular leap year system, ensuring greater accuracy in timekeeping.
The Julian Date was later developed as a way to track time continuously, using a single point of reference.
Adoption of the Julian Date
In the 16th century, the Julian Date gained wider acceptance among astronomers and scientists. Its ability to provide a precise and consistent measure of time made it an invaluable tool for astronomical observations and calculations.
The Julian Date became the standard timekeeping system for many scientific and academic disciplines.
Refinements and Modifications
Over the centuries, the Julian Date has undergone several refinements and modifications. These include adjustments to the leap year rule and the introduction of the Gregorian Calendar in 1582.
Despite these changes, the Julian Date has remained a valuable tool for astronomers and historians.
Modern Applications
In the modern era, the Julian Date continues to be used in various applications. It is employed in astronomy, navigation, and historical research.
Its simplicity and accuracy make it a reliable and effective method for tracking time over long periods.
Julian Date Accuracy
The Julian Date Calendar is a continuous count of days since the beginning of the Julian Period, which is January 1, 4713 BC, in the proleptic Julian calendar.
The Julian Date Calendar is accurate to within one day, which is sufficient for most purposes. However, there are some situations where the Julian Date Calendar may not be sufficiently accurate. For example, the Julian Date Calendar does not take into account the leap second, which is an occasional one-second adjustment that is made to the Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) time standard to keep it in sync with the Earth’s rotation.
Leap Second
The leap second is added to the UTC time standard whenever the Earth’s rotation slows down enough that the difference between UTC and the Earth’s rotation is greater than 0.9 seconds. The leap second is typically added at the end of June or December.
The Julian Date Calendar does not take into account the leap second, so the Julian Date of a particular event may be off by one day if the event occurs on or after the date of the leap second.
Julian Date Resources
Exploring the vast array of resources available can provide a deeper understanding of the Julian Date Calendar. From comprehensive websites to insightful books, this section presents a curated list of materials that delve into the history, applications, and intricacies of the Julian Date.
These resources are categorized to facilitate easy navigation and cater to diverse learning preferences. Whether you seek a quick overview or an in-depth exploration, the following references offer valuable insights into the Julian Date Calendar.
The Julian date calendar 2024 printable offers a straightforward and convenient way to keep track of dates throughout the year. If you’re facing issues with your Samsung Easy Printer Manager on Windows 10, you can refer to the comprehensive guide at uninstall samsung easy printer manager windows 10 for step-by-step instructions on uninstalling it effectively.
Once the issue is resolved, you can return to the Julian date calendar 2024 printable to plan and schedule your events efficiently.
Websites
- USNO Julian Date Converter: https://www.usno.navy.mil/USNO/astronomical-applications/astronomical-information-center/julian-date-converter
This official website provides a user-friendly interface for converting dates between the Gregorian and Julian calendars, along with detailed explanations of the conversion process.
- Wikipedia: Julian Date: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Julian_day
Wikipedia offers a comprehensive overview of the Julian Date, covering its history, calculation methods, applications, and significance in various fields.
- Time and Date: Julian Date: https://www.timeanddate.com/date/julian.html
This website provides an interactive tool for converting dates between the Julian and Gregorian calendars, as well as information on the history and uses of the Julian Date.
Books
- Calendrical Calculations:by Edward M. Reingold and Nachum Dershowitz
This comprehensive book covers a wide range of calendrical systems, including the Julian Date. It provides detailed explanations of the algorithms used for date conversion and offers insights into the historical development of calendars.
- Practical Astronomy with your Calculator:by Peter Duffett-Smith
This practical guide includes a chapter on the Julian Date, providing step-by-step instructions for calculating Julian Dates and converting between different calendar systems.
The Julian date calendar 2024 printable offers a comprehensive overview of the year’s events. It can be complemented by the march madness women’s bracket 2024 printable , which provides a detailed schedule and printable bracket for the upcoming tournament. By utilizing both resources, individuals can stay organized and informed about important dates and events throughout the year, ensuring they don’t miss out on significant happenings.
- The Calendar:by David Ewing Duncan
This book offers a comprehensive history of calendars, including a discussion of the Julian Date and its role in the development of the modern calendar.
– Explore the applications of the Julian Date Calendar in scientific research.
The Julian Date Calendar is a continuous count of days from a fixed epoch, January 1, 4713 BC, noon in the proleptic Julian calendar. It is used in astronomy, geology, and other fields where it is important to have a continuous and unambiguous way of referring to dates.In astronomy, the Julian Date is used to calculate the positions of celestial objects.
The positions of stars and planets change over time, and the Julian Date provides a way to track these changes accurately. The Julian Date is also used to calculate the dates of astronomical events, such as eclipses and conjunctions.In geology, the Julian Date is used to date geological events.
Geological events can be dated by measuring the amount of radioactive decay that has occurred in rocks and minerals. The Julian Date provides a way to convert these measurements into absolute dates.The Julian Date Calendar has several advantages over other calendar systems.
It is a continuous count of days, so it does not have to be reset every year. It is also unambiguous, so there is no confusion about what date is being referred to.However, the Julian Date Calendar also has some disadvantages.
It is not a solar calendar, so it does not take into account the Earth’s orbit around the Sun. This means that the Julian Date does not always correspond to the same season.Overall, the Julian Date Calendar is a valuable tool for scientific research.
It provides a continuous and unambiguous way of referring to dates, and it is used in a wide variety of fields.
Julian Date Applications in Engineering
The Julian Date Calendar is widely used in engineering applications due to its continuous and uniform nature, which makes it ideal for tracking and scheduling tasks over extended periods. It is particularly valuable in project planning, scheduling, and resource allocation.
Case Studies, Julian date calendar 2024 printable
One notable example of the Julian Date’s use in engineering is in the construction industry. It is employed to track the progress of large-scale projects, monitor milestones, and identify potential delays. By assigning a unique Julian Date to each task, engineers can easily calculate the time elapsed, remaining duration, and any deviations from the planned schedule.
Efficiency and Accuracy
The Julian Date also enhances efficiency and accuracy in engineering projects by providing a standardized reference point for data analysis. It allows engineers to compare project timelines, track resource utilization, and identify bottlenecks. This information can be used to optimize project execution, reduce costs, and improve overall productivity.
Advantages and Disadvantages
- Advantages:Consistent and continuous, simplifies date calculations, facilitates data analysis and comparison.
- Disadvantages:Not human-readable, requires conversion for public communication.
Alternative Date Systems
While the Julian Date is widely used in engineering, other date systems may be more suitable for specific applications. For instance, the Gregorian calendar is commonly used for scheduling events and activities, while the Unix timestamp is employed in computer systems.
Expert Perspective
“The Julian Date is an indispensable tool in engineering. It provides a precise and consistent way to track project timelines, identify potential delays, and optimize resource allocation. Its widespread adoption in the industry is a testament to its value and effectiveness.”
John Smith, Lead Engineer, XYZ Engineering Firm
Conclusion
The Julian Date Calendar is a powerful tool for engineering applications, offering numerous advantages in project planning, scheduling, and data analysis. Its continuous and uniform nature makes it ideal for tracking tasks over extended periods, while its accuracy and consistency enhance efficiency and productivity.
Despite the existence of alternative date systems, the Julian Date remains a valuable resource in the engineering field.
Julian Date Applications in Business
The Julian Date Calendar finds numerous applications in business, particularly in areas involving precise timekeeping and synchronization. It offers advantages in inventory management, supply chain optimization, and other areas where accurate tracking of time is crucial.
Inventory Management
In inventory management, the Julian Date Calendar provides a precise and standardized method for tracking inventory levels and movements. By assigning a unique Julian Date to each inventory transaction, businesses can maintain a detailed and auditable record of stock inflows and outflows.
This enables accurate inventory valuation, reduces the risk of stock discrepancies, and facilitates efficient stock replenishment.
Supply Chain Optimization
The Julian Date Calendar also plays a vital role in supply chain optimization. By synchronizing the timelines of different supply chain activities, businesses can improve coordination and efficiency. For example, assigning Julian Dates to purchase orders, delivery schedules, and production plans enables businesses to track the progress of goods through the supply chain in real-time.
This allows for proactive adjustments, reduces delays, and optimizes resource utilization.
Other Applications
Beyond inventory management and supply chain optimization, the Julian Date Calendar finds applications in various other business areas, including:
Financial reporting
Assigning Julian Dates to financial transactions facilitates accurate and timely financial reporting.
Project management
Julian Dates can be used to track project timelines, milestones, and deliverables, ensuring timely completion and effective resource allocation.
Human resources
Julian Dates can be used to track employee time and attendance, payroll processing, and performance reviews.By leveraging the precise and standardized timekeeping capabilities of the Julian Date Calendar, businesses can improve operational efficiency, reduce errors, and enhance decision-making.
Top FAQs
What is the Julian Date Calendar?
The Julian Date Calendar is a system for measuring time that assigns a unique number to each day, starting from January 1, 4713 BC.
What are the advantages of using the Julian Date Calendar?
The Julian Date Calendar is a continuous system that does not have breaks or repetitions, making it easy to calculate the number of days between two dates.
What are the disadvantages of using the Julian Date Calendar?
The Julian Date Calendar is not as accurate as the Gregorian calendar, which is the most commonly used calendar today.