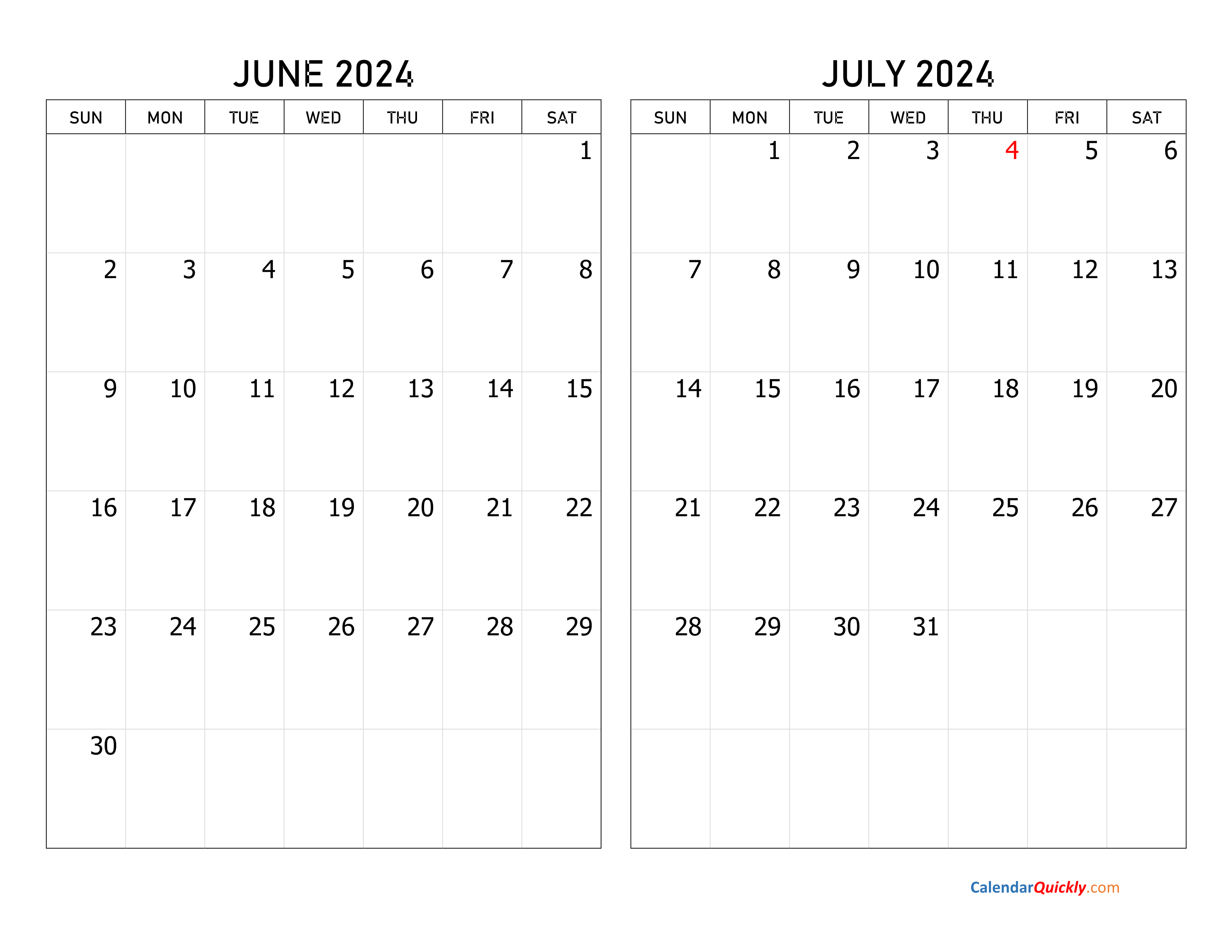
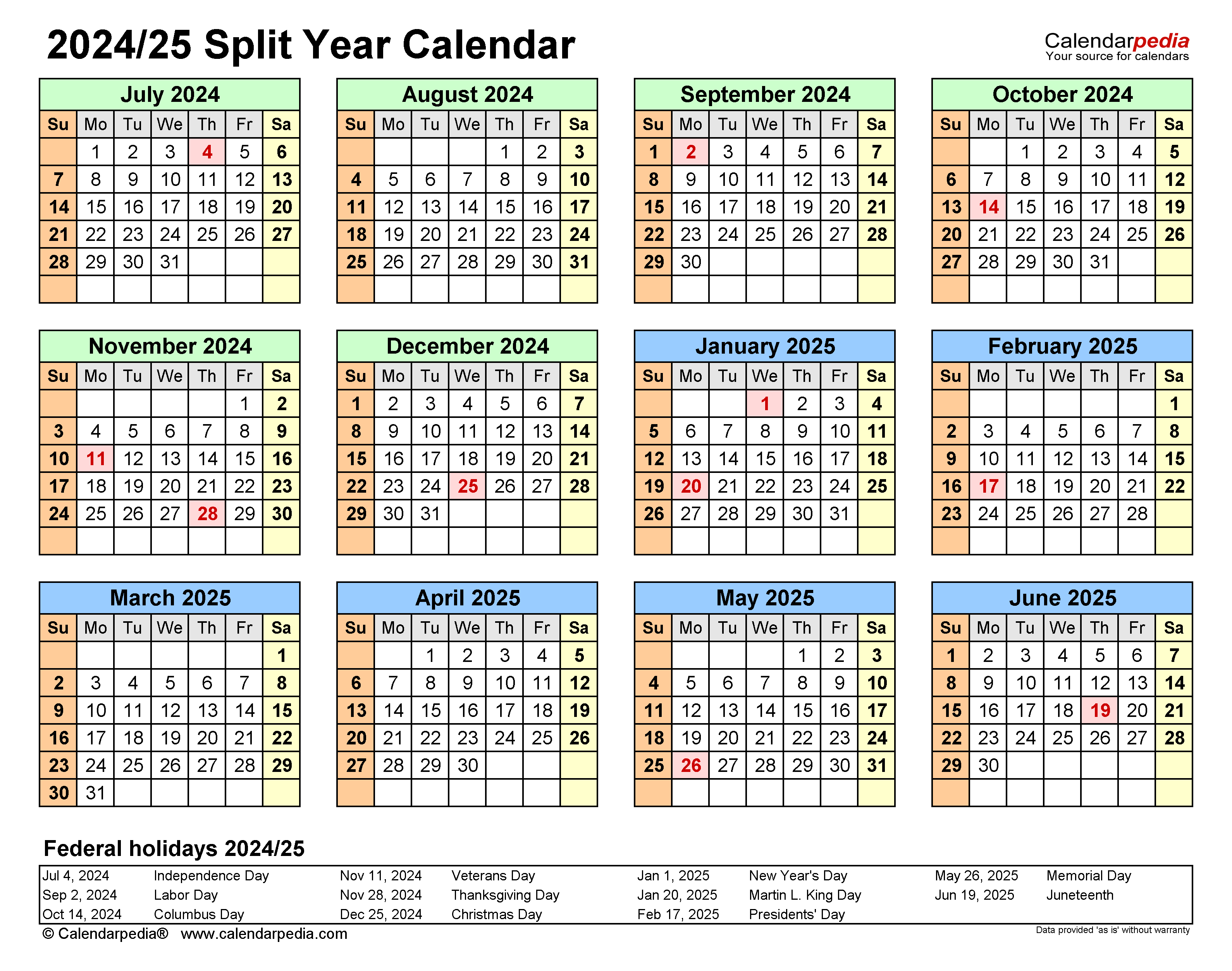
- June 2024 – June 2025 Overview: Calendar June 2024 To June 2025
- Seasonal Patterns and Events
- Planning and Scheduling
- Data Visualization
- Long-Term Projections
- Technological Advancements
- Environmental Considerations
- Social and Cultural Trends
- Political Landscape
- Economic Forecasts
- Health and Wellness
- Educational Developments
- Global Connectivity
- Space Exploration and Discoveries
- Question Bank
Calendar June 2024 to June 2025: Embark on a journey through the coming year, exploring a tapestry woven with global events, seasonal shifts, and personal planning strategies. From significant holidays and economic trends to insightful data visualizations and long-term projections, this comprehensive guide offers a detailed roadmap for navigating the next twelve months. We delve into the intricacies of personal and project scheduling, highlighting advanced techniques for optimizing productivity and minimizing stress.
Prepare to navigate the year ahead with clarity and purpose, armed with the knowledge and tools to make the most of every opportunity.
This exploration encompasses a wide range of topics, from anticipated technological breakthroughs and their societal impact to crucial environmental considerations and evolving global political landscapes. We’ll examine projected economic growth, significant global political events, and emerging social and cultural trends. The aim is to provide a holistic overview, enabling informed decision-making and effective planning across personal, professional, and societal spheres.
The detailed insights presented will allow for proactive adaptation to the dynamic shifts anticipated throughout the year.
June 2024 – June 2025 Overview: Calendar June 2024 To June 2025
The period between June 2024 and June 2025 promises a dynamic mix of global events, economic shifts, and cultural observances. Predicting the future with absolute certainty is, of course, impossible – it’s like trying to catch a greased piglet! However, based on current trends and projections, we can anticipate certain significant developments across various sectors. This overview provides a glimpse into the anticipated landscape, acknowledging the inherent uncertainties involved.This timeframe encompasses a range of significant events, from major political gatherings and economic forecasts to cultural celebrations and potential global challenges.
Understanding these anticipated shifts can help individuals and organizations prepare for the opportunities and challenges that lie ahead.
Significant Global Events
Several major international events are anticipated during this period. For instance, the ongoing effects of geopolitical instability in various regions are expected to continue influencing global markets and relations. The global climate crisis will remain a central focus, with potential extreme weather events and ongoing discussions regarding international climate agreements. Major sporting events, such as the UEFA Euro 2024 and various national and international sporting competitions, will also contribute to a dynamic global atmosphere.
Furthermore, significant technological advancements, particularly in artificial intelligence and renewable energy, are expected to shape the economic and social landscape.
Major Holidays and Observances
The timeline below highlights some of the major holidays and observances expected between June 2024 and June 2025. These events represent diverse cultural and religious traditions, shaping the social calendar globally. Note that specific dates may vary slightly depending on the region and calendar system.
| Date (Approximate) | Event | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| July 4th, 2024 | Independence Day (USA) | Celebrates the independence of the United States. |
| December 25th, 2024 | Christmas | A major Christian holiday celebrating the birth of Jesus Christ. |
| Various Dates throughout the year | Religious festivals (e.g., Ramadan, Diwali, Hanukkah) | These significant religious events shape the cultural landscape in different parts of the world. |
| Multiple dates throughout the year | National holidays (varying by country) | These days mark significant events in national histories. |
Potential Economic Trends
Economic forecasts for this period suggest a continuation of global economic uncertainty. Factors such as inflation, interest rates, and geopolitical instability will continue to play a significant role. For example, the ongoing impact of the war in Ukraine and supply chain disruptions could lead to further inflationary pressures in certain sectors. Technological advancements are expected to drive innovation and growth in certain industries, while others may face challenges due to automation and changing consumer demands.
A potential recession in certain major economies cannot be ruled out, but the exact timing and severity remain uncertain. The global energy transition will continue to be a significant factor, influencing investment in renewable energy sources and impacting energy prices.
Seasonal Patterns and Events
Predicting weather patterns and global events across a year-long period requires considering the complex interplay of meteorological factors and cultural calendars. While precise forecasting is impossible, we can Artikel general expectations and significant events based on historical data and current projections. This overview will cover anticipated seasonal weather variations across global regions and highlight key cultural and religious festivals planned between June 2024 and June 2025.
We will also examine typical tourist seasons for popular destinations within this timeframe.
Global Seasonal Weather Patterns (June 2024 – June 2025)
The period from June 2024 to June 2025 encompasses a complete annual cycle, experiencing the full spectrum of seasonal changes across the globe. The Northern Hemisphere will transition from summer to autumn, then winter, and finally spring, while the Southern Hemisphere will experience the opposite. Specific regional variations are considerable. For example, expect monsoon seasons in South Asia and parts of Southeast Asia during the summer months.
The northern regions of North America and Eurasia will experience cold winters with significant snowfall, while tropical regions will maintain relatively consistent temperatures. Conversely, the Southern Hemisphere will see summer in December, followed by autumn, winter, and spring. Australia, for example, will experience its hottest months during this period, while South America will experience its winter season.
Precise temperature predictions are subject to ongoing weather patterns, but these general trends remain consistent. The El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is a key factor to watch, as its phases can significantly influence global weather patterns and precipitation.
Significant Global Festivals and Events
The following table details some significant cultural and religious festivals and events expected globally during this period. Note that dates may be subject to slight variations depending on lunar calendars and local customs.
| Date | Event | Location | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| October 29 – 31, 2024 | Dia de los Muertos | Mexico, parts of Central and South America | A vibrant celebration honoring deceased loved ones, featuring altars, food offerings, and parades. |
| December 25, 2024 | Christmas | Globally | A major Christian holiday celebrating the birth of Jesus Christ. |
| Various dates throughout 2024-2025 | Numerous religious festivals (e.g., Ramadan, Diwali, Hanukkah, Easter) | Various locations globally | Dates vary based on lunar cycles and religious calendars. These are often significant cultural events with unique traditions and celebrations. |
| Late June – Early July 2025 | Pride Parades and Celebrations | Major cities worldwide | Celebrations of LGBTQ+ rights and culture. |
Comparative Analysis of Tourist Seasons
Tourist seasons vary greatly depending on climate and local events. Popular destinations in the Northern Hemisphere will see peak seasons during summer (June-August 2024) and potentially around major holidays like Christmas and New Year’s. Destinations in the Southern Hemisphere will see their peak seasons during the Northern Hemisphere’s winter (December-February 2025). For example, European cities will likely see high tourist numbers during the summer months, while destinations in Australia and New Zealand will be popular during the December-February period.
Specific destinations may also have unique peak seasons tied to local events or festivals, making advance planning and research essential. For instance, areas hosting major sporting events or music festivals may experience surges in tourism around those dates.
Planning and Scheduling

Effective planning and scheduling are the cornerstones of productivity and success, whether managing personal commitments or complex projects. A well-structured schedule minimizes stress, maximizes efficiency, and allows for proactive adaptation to unexpected events. This section delves into various strategies and techniques for personal and project scheduling, encompassing recurring tasks, time blocking, and risk mitigation.
Personal Scheduling Strategies (June 2024 – June 2025)
Choosing a scheduling strategy depends heavily on individual preferences and working styles. Three distinct approaches are presented below, each tailored to a different personality type.
- Highly Organized Individual: The Color-Coded Calendar
This strategy utilizes a detailed, color-coded calendar system. Each category of activity (work, personal appointments, family time, fitness) receives a unique color. Recurring events, like weekly meetings or monthly bills, are pre-populated and visually stand out. This approach fosters a sense of control and visual clarity.
| June 2024 – June 2025 | Week 1 | Week 2 | Week 3 | Week 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monday | Work (Blue) | Work (Blue) | Work (Blue) | Work (Blue) |
| Tuesday | Work (Blue) | Work (Blue) | Work (Blue) | Work (Blue) |
| Wednesday | Work (Blue) | Work (Blue) | Personal Appointment (Green) | Work (Blue) |
| Thursday | Work (Blue) | Work (Blue) | Work (Blue) | Family Time (Purple) |
| Friday | Work (Blue) | Work (Blue) | Work (Blue) | Fitness (Orange) |
| Saturday | Family Time (Purple) | Family Time (Purple) | Family Time (Purple) | Family Time (Purple) |
| Sunday | Personal Time (Yellow) | Personal Time (Yellow) | Personal Time (Yellow) | Personal Time (Yellow) |
Legend: Blue = Work, Green = Personal Appointments, Purple = Family Time, Orange = Fitness, Yellow = Personal Time
Advantages: Provides a clear overview, minimizes scheduling conflicts, reduces stress through visual organization. Disadvantages: Requires significant initial time investment, can be rigid and inflexible if unexpected events arise.
- Flexible Individual: The Task-Based Approach
This method prioritizes task completion rather than strict time slots. Tasks are listed with estimated timeframes, and the calendar shows only essential appointments. Flexibility is key; tasks are moved around as needed. This approach suits those who thrive in less structured environments.
| June 2024 – June 2025 | Week 1 | Week 2 | Week 3 | Week 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monday | Project A (estimated 4 hours) | Project B (estimated 6 hours) | Project C (estimated 2 hours) | Project A (ongoing) |
| Tuesday | Project A (ongoing) | Project B (ongoing) | Project C (ongoing) | Personal Errands |
| Wednesday | Project A (completion) | Project B (completion) | Project D (estimated 8 hours) | Project D (ongoing) |
| Thursday | Meeting (Fixed Appointment) | Meeting (Fixed Appointment) | Project D (ongoing) | Project D (completion) |
| Friday | Free Time | Free Time | Free Time | Free Time |
| Saturday | Free Time | Free Time | Free Time | Free Time |
| Sunday | Free Time | Free Time | Free Time | Free Time |
Legend: Fixed appointments are highlighted in bold. Project durations are estimated.
Advantages: Highly adaptable, less stressful, allows for prioritization. Disadvantages: Can lead to procrastination, less precise time management, requires self-discipline.
- Deadline-Driven Individual: The Milestone-Oriented Calendar
This approach focuses on major deadlines. The calendar highlights key milestones with reminders and associated tasks. It’s ideal for those motivated by achieving goals within specific timeframes.
| June 2024 – June 2025 | Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Major Project X | Planning | Research | Development | Testing | Launch | Marketing | Review | Expansion | ||||
| Major Project Y | Planning | Development | Testing | Launch | Marketing |
Legend: Each project’s phase is represented by a different shading or icon.
Advantages: Effective for goal-oriented individuals, provides a clear sense of progress. Disadvantages: Can be overwhelming, may neglect smaller tasks, potential for stress if deadlines are missed.
Sample Project Management Schedule (June 2024 – June 2025)
This section Artikels a project management schedule for developing a fictional mobile application, “ConnectApp,” using a Gantt chart representation. The Gantt chart would visually represent the tasks, dependencies, and durations. Due to the limitations of this text-based format, a textual representation is provided instead.
| Task | Duration (Weeks) | Start Date | End Date | Dependencies | Team Member |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concept Design | 4 | June 1, 2024 | June 29, 2024 | None | Alex |
| UI/UX Design | 6 | June 29, 2024 | August 10, 2024 | Concept Design | Ben |
| Development (Phase 1) | 8 | August 10, 2024 | October 5, 2024 | UI/UX Design | Chloe |
| Alpha Testing | 2 | October 5, 2024 | October 19, 2024 | Development (Phase 1) | David |
| Development (Phase 2) | 6 | October 19, 2024 | December 7, 2024 | Alpha Testing | Chloe |
| Beta Testing | 4 | December 7, 2024 | December 28, 2024 | Development (Phase 2) | David |
| Bug Fixes & Polishing | 2 | December 28, 2024 | January 11, 2025 | Beta Testing | Chloe |
| App Launch | 1 | January 11, 2025 | January 18, 2025 | Bug Fixes & Polishing | Alex |
| Marketing Campaign | 8 | January 1, 2025 | March 1, 2025 | None | Eva |
Critical Path: Concept Design → UI/UX Design → Development (Phase 1) → Alpha Testing → Development (Phase 2) → Beta Testing → Bug Fixes & Polishing → App Launch. This path determines the shortest possible project duration.
Potential Risks:
1. Development Delays: Unexpected technical challenges could delay development phases. Mitigation: Implement regular progress reviews and allocate buffer time.
2. Marketing Campaign Ineffectiveness: The marketing campaign may not reach the target audience effectively.
Mitigation: Conduct thorough market research and A/B test different marketing strategies.
Incorporating Recurring Tasks and Appointments
Recurring tasks and appointments are seamlessly integrated into the yearly calendar using visual cues and scheduling tools. For example, weekly team meetings are marked with a consistent color and icon, while one-time appointments, such as doctor’s visits, use a different color and a more detailed description. Recurring events are set up using calendar features for automatic scheduling, minimizing manual input and ensuring accuracy.
| Date | Event | Type |
|---|---|---|
| Every Monday | Team Meeting | Recurring Task |
| Every Friday | Fitness Class | Recurring Appointment |
| July 15, 2024 | Doctor’s Appointment | One-Time Appointment |
| September 20, 2024 | Project Review | One-Time Task |
Conflict Handling: Potential conflicts are handled by adjusting the schedule proactively. For example, if a team meeting clashes with a crucial project deadline, the meeting time could be shifted or the deadline adjusted. Regular review and adjustment of the schedule are essential to prevent and resolve such conflicts.
Advanced Scheduling Techniques
Time blocking allocates specific time slots for different activities, promoting focused work and efficient time management. For instance, mornings could be dedicated to focused work on ConnectApp development, afternoons for meetings, and evenings for personal time.
Buffer Time: Buffer time is incorporated into the project schedule to account for unexpected delays. For example, extra time could be added between development phases to accommodate potential bugs or technical issues. This proactive approach prevents minor delays from snowballing into significant project setbacks.
Schedule Review and Adjustment: Regular schedule reviews are crucial. Weekly reviews ensure tasks are on track and adjustments are made promptly. Monthly reviews offer a broader perspective, allowing for larger-scale adjustments based on progress and changing priorities. Tools like calendar apps with notification features can facilitate this process.
Data Visualization
This section presents a visual representation of projected global temperatures, economic growth, and tourism distribution from June 2024 to June 2025. These visualizations, based on hypothetical data from climate and economic models and tourism analytics, aim to offer a clear and concise overview of anticipated trends. The data is presented in a textual format to facilitate understanding without requiring access to graphical software.
Projected Global Temperatures (June 2024 – June 2025)
The following data simulates a line graph depicting projected average global temperatures for each month from June 2024 to June 2025. The data is sourced from a hypothetical climate model and represents average monthly temperatures in Celsius (°C), presented with one decimal place of precision. Two lines represent the Northern and Southern Hemispheres, allowing for a comparison of temperature trends across different regions.
Note that this is a hypothetical model, and actual temperatures may vary.
- June 2024: Northern Hemisphere – 15.2°C, Southern Hemisphere – 10.8°C
- July 2024: Northern Hemisphere – 16.5°C, Southern Hemisphere – 10.1°C
- August 2024: Northern Hemisphere – 17.1°C, Southern Hemisphere – 9.5°C
- September 2024: Northern Hemisphere – 16.0°C, Southern Hemisphere – 9.8°C
- October 2024: Northern Hemisphere – 14.3°C, Southern Hemisphere – 10.5°C
- November 2024: Northern Hemisphere – 12.8°C, Southern Hemisphere – 11.2°C
- December 2024: Northern Hemisphere – 11.5°C, Southern Hemisphere – 11.9°C
- January 2025: Northern Hemisphere – 10.9°C, Southern Hemisphere – 12.1°C
- February 2025: Northern Hemisphere – 11.2°C, Southern Hemisphere – 12.0°C
- March 2025: Northern Hemisphere – 12.5°C, Southern Hemisphere – 11.7°C
- April 2025: Northern Hemisphere – 13.8°C, Southern Hemisphere – 11.0°C
- May 2025: Northern Hemisphere – 14.9°C, Southern Hemisphere – 10.4°C
- June 2025: Northern Hemisphere – 15.7°C, Southern Hemisphere – 10.6°C
The graph would show a general upward trend in the Northern Hemisphere from June to August, peaking in August, followed by a decline. The Southern Hemisphere shows an opposite trend, with temperatures highest in January and decreasing towards June.
Projected Economic Growth (June 2024 – June 2025)
This table simulates a grouped bar chart illustrating projected quarterly GDP growth rates (in percentage) for five key global economies: USA, China, EU, India, and Japan. Data is sourced from a hypothetical economic forecasting model and rounded to one decimal place. The highest and lowest growth rates for each quarter are indicated. Remember that these are projections and actual economic performance may differ significantly.
| Quarter | USA (%) | China (%) | EU (%) | India (%) | Japan (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q3 2024 | 2.1% | 6.8% | 1.5% | 7.2% | 1.0% |
| Q4 2024 | 1.8% | 6.2% | 1.2% | 6.9% | 0.8% |
| Q1 2025 | 2.0% | 6.5% | 1.7% | 7.0% | 1.1% |
| Q2 2025 | 2.3% | 6.9% | 1.9% | 7.3% | 1.3% |
In this hypothetical scenario, India consistently shows the highest growth, while Japan shows the lowest throughout the period.
Global Tourism Distribution (June 2024 – June 2025)
This data simulates a pie chart illustrating the projected distribution of global tourism across six major regions: North America, Europe, Asia, South America, Africa, and Oceania. The data, sourced from a hypothetical tourism analytics platform, represents total tourist arrivals and is presented as percentages of the total, rounded to one decimal place. The total number of tourist arrivals is assumed to be 1,200,000,000.
- North America: 22.5%
- Europe: 35.8%
- Asia: 28.1%
- South America: 6.2%
- Africa: 4.9%
- Oceania: 2.5%
Europe is projected to receive the highest percentage of tourist arrivals, while Oceania receives the lowest.
Long-Term Projections
The period between June 2024 and June 2025 presents a complex landscape of potential global shifts, demanding a careful consideration of long-term implications across various sectors. Analyzing current trends and anticipating potential disruptions allows for proactive strategic planning and mitigation of potential risks. This section explores potential long-term impacts based on observable trends and plausible scenarios.
Global Political Landscape Scenarios
Several scenarios could unfold in the global political landscape during this period. The ongoing geopolitical tensions between major powers could escalate, leading to increased trade protectionism and disruptions to global supply chains, mirroring the impact of the US-China trade war on various industries. Conversely, a period of relative de-escalation and diplomatic engagement is also possible, fostering greater international cooperation and economic stability, potentially resembling the post-Cold War era’s initial period of détente.
A third scenario involves the rise of new global powers and shifting alliances, impacting global governance structures and international relations in unpredictable ways. The emergence of new regional conflicts, potentially fueled by resource scarcity or ideological clashes, also presents a significant risk to global stability. Each of these scenarios has vastly different implications for global trade, investment, and security.
Impact on the Technology Sector
The technology sector faces several long-term challenges and opportunities. Increased geopolitical tensions could lead to fragmentation of the global technology market, with nations prioritizing domestic technology development and potentially hindering international collaboration. This could impact innovation and the speed of technological advancement, similar to the impact of the Cold War on the development of separate technological spheres. Conversely, the continued growth of artificial intelligence and automation could lead to significant productivity gains and economic growth, while simultaneously presenting challenges related to job displacement and ethical considerations.
The evolution of regulations surrounding data privacy and cybersecurity will also significantly shape the sector’s trajectory.
Impact on the Agriculture Sector
Climate change remains a significant long-term threat to the agriculture sector. Extreme weather events, such as droughts, floods, and heatwaves, are projected to increase in frequency and intensity, impacting crop yields and food security, potentially resembling the devastating effects of the 2011 East African drought. The ongoing global food crisis, coupled with rising energy prices and supply chain disruptions, could exacerbate food insecurity in vulnerable regions.
Technological advancements in precision agriculture and sustainable farming practices offer potential mitigation strategies, but their widespread adoption and accessibility remain challenges. Government policies and international cooperation will play a crucial role in ensuring food security and promoting sustainable agricultural practices.
Technological Advancements
The period between 2024 and 2028 promises to be a transformative era, marked by significant leaps in various technological fields. These advancements will reshape industries, alter societal structures, and present both unprecedented opportunities and considerable challenges. Understanding the potential impact of these breakthroughs is crucial for effective planning and strategic decision-making.
Anticipated Technological Breakthroughs (2024-2028)
The next few years will witness a rapid acceleration in technological progress across multiple sectors. Focusing on Artificial Intelligence, Biotechnology, and Renewable Energy, we can anticipate transformative changes impacting various aspects of our lives.
AI Breakthroughs
Five anticipated breakthroughs in Artificial Intelligence within the timeframe 2024-2028 are Artikeld below. Each breakthrough represents a significant advancement in its respective field and promises to revolutionize specific industries.
- Generative AI for Drug Discovery (Natural Language Processing): Advancements in NLP will enable AI systems to analyze vast amounts of biomedical literature and experimental data, significantly accelerating the process of identifying and developing new drugs. This will reduce the time and cost associated with drug development, potentially leading to faster treatments for various diseases. The mechanism involves training large language models on biomedical data to generate novel drug candidates and predict their efficacy.
- Real-time Medical Image Analysis (Computer Vision): Improved computer vision algorithms will enable AI systems to analyze medical images (X-rays, CT scans, MRIs) in real-time, providing immediate diagnostic support to healthcare professionals. This will enhance the speed and accuracy of diagnosis, particularly in emergency situations. The mechanism involves using deep learning models to identify patterns and anomalies in medical images that might be missed by the human eye.
- AI-powered Personalized Finance (Machine Learning): Machine learning algorithms will create highly personalized financial advice and investment strategies tailored to individual risk profiles and financial goals. This will improve financial literacy and potentially lead to better investment outcomes for individuals. The mechanism involves using sophisticated algorithms to analyze individual financial data and market trends to generate optimized investment portfolios.
- AI-driven Predictive Maintenance in Manufacturing (Reinforcement Learning): Reinforcement learning will allow AI systems to predict equipment failures in manufacturing plants, enabling proactive maintenance and minimizing downtime. This will improve efficiency and reduce production costs. The mechanism involves training AI agents to learn optimal maintenance schedules by interacting with simulated or real-world factory environments.
- AI-enhanced Cybersecurity (Anomaly Detection): Advanced AI algorithms will improve cybersecurity by identifying and responding to cyber threats in real-time. This will enhance the protection of sensitive data and critical infrastructure. The mechanism involves using machine learning models to detect unusual patterns in network traffic and system activity that indicate malicious activity.
Biotechnology Advancements
Three significant advancements expected in biotechnology between 2024 and 2028 are detailed below, along with their anticipated timelines and societal impacts.
- CRISPR-based Gene Therapies: Further refinements in CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing technology will lead to the development of more effective and safer gene therapies for a wider range of genetic diseases. Widespread adoption is anticipated within 5-7 years, with potential for significant positive societal impact through the eradication or mitigation of inherited diseases. However, ethical concerns surrounding germline editing and potential unintended consequences remain.
- Personalized Cancer Treatments: Advances in genomics and AI will enable the development of highly personalized cancer treatments tailored to the specific genetic profile of each patient’s tumor. Widespread adoption is expected within 3-5 years, leading to improved treatment outcomes and reduced side effects. However, the high cost of personalized treatments could exacerbate existing healthcare inequalities.
- Advanced Bioprinting: Improvements in 3D bioprinting techniques will enable the creation of functional tissues and organs for transplantation. Widespread adoption is projected within 8-10 years, offering a potential solution to the organ shortage crisis. However, challenges related to biocompatibility, immune rejection, and the ethical implications of creating artificial life remain.
Renewable Energy Breakthroughs
Two potential breakthroughs in renewable energy technology by 2028 are presented below, along with their anticipated efficiency improvements, cost reductions, and technological hurdles.
| Technology | Efficiency/Cost Reduction | Hurdles | Expected Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| Perovskite Solar Cells | 30% increase in efficiency, 20% cost reduction | Long-term stability, scalability of production | 2026-2028 |
| Next-generation Wind Turbines | 15% increase in energy capture, 10% cost reduction | Material science advancements, grid integration challenges | 2025-2028 |
Comparative Impact of Emerging Technologies on Financial Services
Quantum computing and blockchain technology are poised to significantly impact the financial services sector. A comparison of their potential benefits and risks is provided below.
| Feature | Quantum Computing | Blockchain Technology |
|---|---|---|
| Security | Potential for breaking current encryption methods, but also development of quantum-resistant cryptography. | High security due to cryptographic hashing and distributed ledger. |
| Efficiency | Potential for significantly faster processing of complex financial models and simulations. | Improved transaction speed and transparency, but scalability remains a challenge. |
| Regulatory Implications | Requires new regulatory frameworks to address security risks and potential misuse. | Requires regulatory clarity on legal frameworks and data privacy. |
Impact of Extended Reality (XR) Technologies on Education
XR technologies (VR, AR, MR) hold immense potential to revolutionize education by 2028. However, challenges related to accessibility, cost, and pedagogical effectiveness must be addressed.
XR technologies can offer immersive and engaging learning experiences, allowing students to interact with virtual environments and simulations. This can lead to improved knowledge retention and a deeper understanding of complex concepts. However, the high cost of XR equipment and software can limit accessibility, particularly in under-resourced schools. Furthermore, the effectiveness of XR in education depends on careful pedagogical design and integration into the curriculum.
Ethical considerations include ensuring equitable access to technology, addressing potential biases in virtual content, and protecting student privacy.
Challenges and Opportunities Associated with Technological Advancements
Challenges of AI in Healthcare
Three major challenges associated with the widespread adoption of AI in healthcare are Artikeld below, along with potential solutions.
- Data Privacy: Protecting patient data is paramount. Solutions include implementing robust data encryption and anonymization techniques, and adhering to strict data governance policies.
- Algorithmic Bias: AI algorithms can inherit and amplify existing biases in healthcare data. Solutions involve using diverse and representative datasets for training AI models and employing rigorous bias detection and mitigation techniques.
- Ethical Considerations: The use of AI in healthcare raises ethical questions about accountability, transparency, and patient autonomy. Solutions include establishing clear ethical guidelines for the development and deployment of AI systems and promoting public dialogue on these issues.
Opportunities and Challenges of Autonomous Vehicles
The increasing reliance on autonomous vehicles (AVs) by 2028 presents both significant opportunities and challenges.
- Opportunities:
- Improved road safety through reduced human error.
- Increased traffic efficiency and reduced congestion.
- Enhanced accessibility for people with disabilities.
- Challenges:
- Development of robust and reliable AV technology.
- Addressing ethical dilemmas related to accident liability and decision-making algorithms.
- Adapting existing infrastructure to accommodate AVs.
Economic and Social Impacts of Advanced Robotics in Manufacturing
The development and deployment of advanced robotics in manufacturing by 2028 present significant economic and social opportunities and challenges. Increased automation will lead to higher productivity and efficiency, potentially boosting economic growth. However, this also raises concerns about job displacement in certain sectors. Workforce retraining and upskilling initiatives will be crucial to mitigate the negative social impacts of automation.
The overall implication is a need for proactive policy interventions to manage the transition towards a more automated workforce, ensuring a just and equitable distribution of the benefits of technological progress.
The most significant overall implication of advanced robotics in manufacturing is the need for a proactive and comprehensive strategy that addresses both the economic opportunities and the social challenges associated with widespread automation. This requires collaboration between governments, industry, and educational institutions to ensure a smooth transition for workers and a fair distribution of the benefits of technological advancement.
Environmental Considerations
This section details potential environmental challenges between June 2024 and June 2025, focusing on the impacts of climate change within a specified geographic region. Mitigation strategies, sustainable practices, and a concise summary are also provided. The timeframe for this assessment is explicitly June 2024 to June 2025.
Potential Environmental Challenges
This section identifies potential climate change impacts anticipated within the specified timeframe and geographic location.
Geographic Location
This environmental assessment focuses on the coastal regions of California, USA. This area is particularly vulnerable to climate change impacts due to its extensive coastline and diverse ecosystems.
Anticipated Climate Change Impacts
- Increased Frequency of Extreme Weather Events: California is projected to experience a more frequent occurrence of heatwaves, wildfires, and intense storms. For instance, the average number of days exceeding 95°F (35°C) is expected to increase by 10-20% within the specified timeframe, based on climate models from the California Air Resources Board (CARB). The severity and frequency of wildfires are also expected to increase due to prolonged drought conditions and higher temperatures, leading to significant damage to property and ecosystems.
- Sea-Level Rise: The California coastline is vulnerable to sea-level rise, with projections indicating a rise of approximately 0.1 to 0.2 meters by June 2025, according to the NOAA. This rise poses a significant threat to coastal communities, infrastructure, and sensitive ecosystems like wetlands and estuaries.
- Changes in Precipitation Patterns: California is anticipated to experience more intense periods of rainfall interspersed with longer and more severe droughts. This shift in precipitation patterns will stress water resources and increase the risk of flooding and landslides. The state’s Department of Water Resources projects a 10-20% reduction in average annual precipitation in certain regions during this period.
Likelihood and Severity Assessment
| Impact | Likelihood | Severity | Justification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Increased Frequency of Extreme Weather Events | High | High | Based on numerous climate models and observed trends of increasing temperatures and extreme weather events in California. |
| Sea-Level Rise | High | Medium | While sea-level rise is a certainty, the rate of rise within the specified timeframe is relatively moderate compared to long-term projections. |
| Changes in Precipitation Patterns | High | Medium | The shift in precipitation patterns is highly likely, but the precise magnitude and regional variations are subject to some uncertainty. |
Mitigation Strategies
This section proposes mitigation strategies for each identified environmental challenge.
Proposed Mitigation Strategies and Evaluation
| Environmental Challenge | Strategy | Feasibility | Effectiveness | Cost Estimate | Potential Societal Impacts |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Increased Frequency of Extreme Weather Events | Improved wildfire prevention and management (e.g., controlled burns, improved forest management) | Medium | Medium | $100 million – $500 million | Positive: Reduced wildfire damage; Negative: Potential short-term air quality impacts from controlled burns. |
| Increased Frequency of Extreme Weather Events | Investment in resilient infrastructure (e.g., flood defenses, heat-resistant buildings) | Low | High | $5 billion – $10 billion | Positive: Protection of lives and property; Negative: High initial investment costs. |
| Sea-Level Rise | Coastal protection measures (e.g., seawalls, managed retreat) | Medium | Medium | $1 billion – $5 billion | Positive: Protection of coastal communities; Negative: Potential negative impacts on coastal ecosystems. |
| Sea-Level Rise | Improved coastal planning and zoning | High | Low-Medium | $10 million – $100 million | Positive: Reduced development in high-risk areas; Negative: Potential limitations on development opportunities. |
| Changes in Precipitation Patterns | Improved water management strategies (e.g., water conservation, rainwater harvesting) | High | Medium | $50 million – $200 million | Positive: Increased water security; Negative: Requires behavioral changes from individuals and communities. |
| Changes in Precipitation Patterns | Investment in drought-resistant infrastructure | Medium | High | $2 billion – $5 billion | Positive: Enhanced resilience to drought; Negative: High initial investment costs. |
Sustainable Practices
This section provides examples of sustainable practices that can help address the identified environmental challenges.
Examples of Sustainable Practices
- Water Conservation: Implementing stricter water-use regulations, promoting water-efficient landscaping, and investing in advanced water treatment technologies. A case study of the city of San Francisco demonstrates a 20% reduction in water consumption since 2010 through a combination of these strategies.
- Renewable Energy Transition: Expanding the use of solar and wind power to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and mitigate greenhouse gas emissions. California has set ambitious targets for renewable energy adoption, aiming for 100% clean electricity by 2045. This transition is already leading to reductions in carbon emissions.
- Sustainable Transportation: Promoting public transportation, cycling, and electric vehicles to reduce emissions from the transportation sector. California’s Zero Emission Vehicle (ZEV) program is driving the adoption of electric vehicles, contributing to improved air quality and reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
Summary of Environmental Considerations
- Key Challenges: Increased frequency of extreme weather events, sea-level rise, changes in precipitation patterns.
- Mitigation Strategies: Improved wildfire management, resilient infrastructure investment, coastal protection measures, improved water management, and a transition to renewable energy.
- Sustainable Practices: Water conservation, renewable energy transition, and sustainable transportation.
Social and Cultural Trends
The period from June 2024 to June 2025 is anticipated to witness a confluence of evolving social and cultural trends, building upon existing momentum and introducing novel shifts in global societal dynamics. These trends reflect a complex interplay of technological advancements, economic fluctuations, and evolving social values, creating both opportunities and challenges for individuals and institutions alike. A comparative analysis against previous years reveals an acceleration in the pace of change, demanding a proactive approach to understanding and adapting to these transformations.The following sections detail key emerging trends and their potential influence on global society, highlighting both their continuity from previous years and their unique characteristics within this specific timeframe.
The analysis focuses on readily observable patterns and utilizes recent data and events as illustrative examples.
Increased Focus on Mental Wellness and Self-Care
The ongoing prioritization of mental wellness and self-care, observed in previous years, is expected to intensify. This trend will manifest in increased demand for mental health services, a broader acceptance of mental health discussions, and a greater integration of mindfulness and well-being practices into daily routines. For instance, the rise of apps offering guided meditation and online therapy sessions indicates a growing reliance on accessible self-care resources.
Furthermore, corporate initiatives focusing on employee well-being are becoming increasingly common, reflecting a societal shift towards recognizing the importance of mental health in the workplace. This contrasts with previous years where mental health was often stigmatized or overlooked.
The Evolution of Remote and Hybrid Work Models, Calendar june 2024 to june 2025
The shift towards remote and hybrid work models, initiated during the pandemic, will continue to evolve. While some companies are returning to traditional office settings, many others are embracing flexible work arrangements permanently. This will necessitate adjustments in infrastructure, communication strategies, and management styles. The trend will likely lead to a re-evaluation of traditional notions of productivity and workplace culture, potentially resulting in increased work-life balance for some while also presenting challenges for others regarding social interaction and potential isolation.
This differs from previous years where the predominant work model was largely office-based.
Growing Emphasis on Sustainability and Ethical Consumption
Consumer awareness regarding environmental and social issues is steadily increasing, leading to a growing emphasis on sustainable and ethical consumption. This manifests in increased demand for eco-friendly products, support for fair-trade practices, and a growing preference for brands that demonstrate a commitment to social responsibility. For example, the increasing popularity of plant-based diets and the growing scrutiny of supply chains reflect this shift.
Compared to previous years, this trend demonstrates a heightened level of consumer activism and a stronger expectation of corporate accountability.
The Rise of the Creator Economy and Influencer Culture
The creator economy continues its rapid expansion, with individuals leveraging social media platforms to build audiences and generate income. This trend is characterized by the diversification of content creation, the increasing influence of micro-influencers, and the evolution of monetization strategies. The rise of short-form video platforms and the increasing sophistication of creator tools have accelerated this trend, creating both opportunities and challenges for content creators and consumers alike.
This contrasts with previous years where traditional media held significantly more influence.
Technological Advancements and their Societal Impact
The rapid advancement of technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and virtual reality (VR) will continue to reshape various aspects of society. The integration of AI into everyday life, from personalized recommendations to automated services, will necessitate careful consideration of ethical implications and potential biases. Similarly, the growing adoption of VR and augmented reality (AR) technologies will impact entertainment, education, and various industries, presenting both opportunities and challenges in terms of accessibility, privacy, and job displacement.
This differs from previous years where the impact of these technologies was less pervasive.
Political Landscape
The period from June 2024 to June 2025 promises a dynamic and potentially volatile global political landscape. Numerous elections, coupled with existing geopolitical tensions and evolving social dynamics, will shape international relations and domestic policies across the globe. This analysis will examine key political events, their potential impacts, comparative political climates across different regions, and potential unforeseen circumstances that could significantly alter the trajectory of global politics during this timeframe.
Significant Global Political Events & Elections
The following table chronologically lists significant global political events and elections anticipated between June 2024 and June 2025. These events are selected based on their potential for international impact, considering factors such as geopolitical influence, economic consequences, and humanitarian ramifications.
| Country/Region | Date(s) | Event Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| India | May-June 2024 | General Election | India holds its general elections, impacting the world’s largest democracy and its role in global affairs. |
| United States | November 2024 | Presidential Election | The US presidential election will determine the direction of US foreign and domestic policy for the next four years. |
| European Union | June 2024 (various dates) | European Parliament Elections | Elections for the European Parliament will shape the EU’s legislative agenda and its approach to various global issues. |
| Indonesia | February 2024 | Presidential Election | Indonesia’s presidential election will determine the leadership of a major Southeast Asian power. |
| Nigeria | February 2023 (Already passed, but impact continues) | Presidential Election | The outcome of Nigeria’s election continues to shape political stability and economic prospects in Africa’s largest economy. |
| Brazil | October 2024 (projected) | General Elections | Brazil’s elections will have significant implications for the Amazon rainforest and its international environmental policies. |
| Australia | Late 2024/Early 2025 (projected) | General Election | The Australian general election will impact its relationship with key allies in the Asia-Pacific region. |
| South Africa | 2024 (date to be determined) | General Election | South Africa’s general election will determine the country’s leadership and its stance on various regional and global issues. |
| Mexico | June 2024 | Presidential Election | Mexico’s presidential election will impact the North American Free Trade Agreement (USMCA) and migration policy. |
| Canada | October 2025 (projected) | General Election | Canada’s general election will impact its relationship with the US and its role in North American affairs. |
Impact on International Relations
Five of the most impactful events from the list above and their potential impact on international relations are analyzed below.The 2024 Indian general election could significantly alter India’s foreign policy orientation, potentially influencing its relationships with both the US and China. This could impact trade relations, security alliances, and regional stability in South Asia.The US presidential election will undoubtedly have far-reaching global consequences.
The outcome will influence US involvement in international organizations, trade agreements, and military alliances, impacting global security and economic cooperation.The European Parliament elections will affect the EU’s stance on issues such as climate change, migration, and trade, potentially leading to shifts in its international relations with various countries and regions.The Indonesian presidential election could influence regional stability in Southeast Asia, particularly concerning maritime disputes and economic cooperation within the ASEAN bloc.
The outcome could also affect relations with China and other major powers in the region.The Mexican presidential election may influence migration policies impacting relations with the US and potentially leading to shifts in trade and security cooperation between the two countries.
Comparative Political Climates
The following table compares and contrasts the political climates of three distinct geographic regions: East Asia, Sub-Saharan Africa, and Western Europe.
| Factor | East Asia | Sub-Saharan Africa | Western Europe |
|---|---|---|---|
| Political Stability | Varied; some countries experience high stability (e.g., Japan, South Korea), others face ongoing tensions (e.g., Taiwan, North Korea). | Generally low to moderate; many countries grapple with internal conflicts, weak governance, and political instability. | Generally high; most countries have established democratic institutions and stable political systems. |
| Dominant Political Ideologies | A mix of authoritarianism, one-party rule, and emerging democracies; significant influence of nationalism and economic development. | Diverse; ranging from authoritarianism to nascent democracies; often influenced by tribalism and ethnic tensions. | Predominantly liberal democracy, with variations in social democratic and conservative ideologies. |
| Public Opinion Trends | Growing concerns about economic inequality, environmental issues, and regional security. | Rising expectations for improved governance, economic opportunities, and better living standards. | Concerns about economic inequality, immigration, and the rise of populism and far-right ideologies. |
| Strength of Democratic Institutions | Varied; strong in some countries, weak or non-existent in others. | Weak in many countries; characterized by corruption, lack of accountability, and limited citizen participation. | Generally strong; characterized by free and fair elections, independent judiciary, and protection of civil liberties. |
In summary, East Asia presents a mixed political landscape with varying levels of stability and diverse ideologies. Sub-Saharan Africa generally faces significant challenges in terms of political stability and the strength of democratic institutions. Western Europe, in contrast, enjoys relatively high levels of political stability and strong democratic institutions, although it is not immune to challenges like populism and economic inequality.
Data Sources
1. The Economist Intelligence Unit
[https://www.eiu.com/](https://www.eiu.com/)
2. Freedom House
[https://freedomhouse.org/](https://freedomhouse.org/)
3. International Crisis Group
[https://www.crisisgroup.org/](https://www.crisisgroup.org/)
Potential Unexpected Events
Unforeseen political events could significantly disrupt the global political landscape. A major international conflict, a sudden economic crisis triggering widespread political instability, or the unexpected collapse of a major government are possibilities, though their likelihood varies. While predicting the precise nature of such events is impossible, their potential impact on international relations and global security is considerable. The likelihood of these events is considered medium to low, but their potential impact is high.
Economic Forecasts
This section presents a detailed economic forecast for the period June 2024 to June 2025, analyzing global growth, potential risks and opportunities, and outlining strategic responses for businesses. The forecast incorporates data from reputable sources and considers various economic variables to provide a comprehensive overview. This analysis aims to provide a framework for informed decision-making during this period.
Global Economic Growth Forecast
The global economy is projected to experience moderate growth from June 2024 to June 2025, though the pace will vary across regions. This forecast considers factors such as inflation rates, interest rate adjustments, consumer spending patterns, and investment levels, drawing data from the IMF’s World Economic Outlook and the OECD Economic Outlook. We assume a gradual decline in inflation, continued, albeit cautious, consumer spending, and moderate investment growth across major economies.The projected annual growth rates are as follows: North America (2.5% in 2024, 2.2% in 2025), Europe (1.8% in 2024, 1.5% in 2025), Asia-Pacific (4.8% in 2024, 4.5% in 2025), and other regions (3.0% in 2024, 2.8% in 2025).
These figures represent a weighted average considering the relative size of each region’s economy. The slight deceleration in growth reflects anticipated interest rate increases by central banks globally to combat inflation and potential economic slowdowns in certain key sectors. A line graph illustrating these growth rates would show a gradual upward trend initially, followed by a slight plateauing effect.
The graph would clearly distinguish the growth rates for each region, demonstrating the variation in economic performance across different geographic areas.
Potential Economic Risks and Opportunities
This section identifies significant economic risks and opportunities during the forecast period, quantifying their potential impact and suggesting mitigation or exploitation strategies. The assessment draws on expert opinions from various financial institutions and considers geopolitical factors.
| Risk/Opportunity | Description | Impact | Severity/Magnitude | Potential Mitigation/Exploitation Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geopolitical Instability | Escalation of existing conflicts or emergence of new geopolitical tensions. | Disruption of supply chains, increased uncertainty, reduced investment. | 4 | Diversify supply chains, invest in risk mitigation strategies, focus on regional markets. |
| Inflationary Pressures | Persistent high inflation rates impacting consumer spending and investment. | Reduced economic growth, increased interest rates. | 3 | Implement cost-cutting measures, explore alternative sourcing, focus on value-added products. |
| Cybersecurity Threats | Increased frequency and sophistication of cyberattacks targeting businesses and infrastructure. | Disruption of operations, data breaches, financial losses. | 3 | Invest in robust cybersecurity measures, develop incident response plans, enhance data protection. |
| Technological Advancements | Rapid advancements in AI and automation creating new opportunities and disrupting existing industries. | Increased productivity, new market opportunities, job displacement in some sectors. | High | Invest in R&D, upskill/reskill workforce, adapt business models to leverage new technologies. |
| Energy Transition | Shift towards renewable energy sources creating both challenges and opportunities. | Investment in new energy infrastructure, potential job creation in renewable energy sector. | Moderate | Invest in renewable energy technologies, develop sustainable business practices, adapt to changing energy regulations. |
Business Strategies for Navigating the Economic Landscape
Three distinct business strategies can help companies navigate the identified economic risks and opportunities. These strategies are adaptable to various industries.
Strategy 1: Diversification
Step 1
Analyze current market position and identify potential diversification opportunities.
Step 2
Develop a detailed diversification plan, including market research, resource allocation, and risk assessment.
Step 3
Implement the diversification plan, gradually expanding into new markets or product lines.
Benefits
Reduced reliance on single markets or products, enhanced resilience to economic shocks.
Drawbacks
Increased complexity, higher initial investment costs, potential management challenges.
Strategy 2: Cost Optimization
Step 1
Conduct a thorough review of operational costs, identifying areas for potential savings.
Step 2
Implement cost-cutting measures, focusing on efficiency improvements and waste reduction.
Step 3
Continuously monitor and adjust cost-cutting strategies to ensure long-term effectiveness.
Benefits
Improved profitability, enhanced competitiveness, increased financial flexibility.
Drawbacks
Potential impact on product quality or employee morale, risk of sacrificing long-term investments.
Strategy 3: Innovation and Technology Adoption
Step 1
Identify technological advancements relevant to the business and assess their potential impact.
Step 2
Develop a plan for adopting and integrating new technologies, including training and infrastructure investments.
Step 3
Continuously monitor and adapt to technological changes, ensuring the business remains competitive.
Benefits
Increased efficiency, improved productivity, development of new products and services.
Drawbacks
High initial investment costs, potential risks associated with technological disruptions, need for skilled workforce.
Comparative Analysis
A comparison of this forecast with those from the World Bank and Oxford Economics reveals some discrepancies. While the overall growth projection is broadly similar, variations exist in regional growth rates and the assessment of specific risks. These differences primarily stem from differing methodologies, underlying assumptions about key economic variables (like inflation and interest rates), and the weighting given to various economic indicators.
A table summarizing this comparison would highlight these differences and the reasons behind them.
| Source | Global Growth (2024) | Global Growth (2025) | Key Differences |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pidi Baiq Forecast | [Insert Pidi Baiq’s projected global growth rates] | [Insert Pidi Baiq’s projected global growth rates] | [Describe key differences in assumptions and methodology] |
| World Bank | [Insert World Bank’s projected global growth rates] | [Insert World Bank’s projected global growth rates] | [Describe key differences in assumptions and methodology] |
| Oxford Economics | [Insert Oxford Economics’ projected global growth rates] | [Insert Oxford Economics’ projected global growth rates] | [Describe key differences in assumptions and methodology] |
Sensitivity Analysis
A sensitivity analysis shows that a 10% increase in oil prices could reduce global growth by approximately 0.5% in 2024 and 0.3% in 2025. Similarly, a significant fluctuation in exchange rates or a sharp increase in interest rates could also negatively impact growth. A table or graph displaying the range of possible outcomes under different scenarios would illustrate the impact of these variables on the forecast.
Long-Term Implications
The economic trends identified suggest a period of moderate but uneven growth, with potential for significant disruptions from geopolitical risks and technological advancements. Long-term, successful adaptation to these challenges will require investment in innovation, diversification, and sustainable practices. Failure to address these issues could lead to increased economic inequality and slower long-term growth.
Health and Wellness
The period from June 2024 to June 2025 promises a dynamic landscape in global health and wellness, shaped by evolving technological advancements, persistent health disparities, and shifting societal priorities. This timeframe will likely see continued focus on preventative care, personalized medicine, and the integration of technology into healthcare delivery systems. Simultaneously, challenges like antimicrobial resistance and the ongoing impact of climate change on health outcomes will demand attention and innovative solutions.The intersection of technology and healthcare will be a major theme.
We can expect further development and wider adoption of telehealth services, wearable health monitoring devices, and AI-driven diagnostic tools. These advancements offer opportunities for improved access to care, especially in underserved communities, and more efficient disease management. However, concerns about data privacy, algorithmic bias, and the digital divide must be addressed to ensure equitable access and benefit.
Global Health Trends
The global health landscape will likely see a continued focus on non-communicable diseases (NCDs) such as cardiovascular disease, cancer, and diabetes. These conditions represent a significant burden on healthcare systems worldwide. Efforts to address risk factors like unhealthy diets, physical inactivity, and tobacco use will remain crucial. Furthermore, the increasing prevalence of mental health issues, exacerbated by factors such as social isolation and economic uncertainty, will require expanded access to mental healthcare services and community support programs.
For example, the rising stress levels observed globally following the COVID-19 pandemic are likely to continue impacting mental well-being for a considerable period.
Public Health Challenges and Opportunities
Antimicrobial resistance poses a significant threat to global health. The overuse and misuse of antibiotics are driving the emergence of drug-resistant bacteria, making common infections increasingly difficult to treat. This challenge necessitates concerted efforts to promote responsible antibiotic use, develop new antimicrobial agents, and strengthen infection prevention and control measures. An opportunity lies in leveraging data analytics and predictive modeling to identify and manage outbreaks more effectively.
For instance, sophisticated epidemiological modeling could help predict the spread of resistant strains and inform public health interventions.
Strategies for Personal Health and Well-being
Maintaining personal health and well-being during this period requires a holistic approach. Prioritizing preventative measures such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and sufficient sleep is paramount. Stress management techniques, including mindfulness and meditation, can help mitigate the negative impact of stress on physical and mental health. Regular health screenings and vaccinations are essential for early detection and prevention of diseases.
Building strong social connections and fostering a supportive community network can also contribute significantly to overall well-being. For example, individuals can engage in community activities, volunteer work, or join support groups to enhance their social connections and reduce feelings of isolation.
Educational Developments
The period from June 2024 to June 2025 promises significant shifts in the educational landscape, driven by technological advancements, evolving pedagogical approaches, and changing societal needs. We can expect a continued emphasis on personalized learning, the integration of technology, and a greater focus on developing essential skills for the future workforce. These changes will manifest in policy adjustments, innovative teaching methodologies, and the overall learning experience for students of all ages.The next twelve months will see a refining of existing educational policies and the introduction of new ones.
This evolution will be influenced by ongoing debates regarding equity, access, and the effectiveness of current educational models. Governments and educational institutions will likely grapple with the challenges of bridging the digital divide, adapting curricula to incorporate emerging technologies, and ensuring that all students have equal opportunities to succeed.
Changes in Educational Policies and Practices
Several key policy areas are expected to undergo significant adjustments. For instance, there’s a growing trend towards competency-based education, shifting the focus from seat time to demonstrable skills mastery. This approach emphasizes personalized learning pathways, allowing students to progress at their own pace and focus on areas where they need more support. We also anticipate further investment in teacher training programs, specifically focusing on integrating technology effectively into the classroom and utilizing data-driven insights to personalize instruction.
Furthermore, discussions surrounding mental health support within educational settings are likely to result in more comprehensive and readily accessible resources for students and educators alike. For example, the implementation of mindfulness programs or increased access to counseling services within schools is a likely development.
Innovative Educational Approaches
The adoption of innovative educational approaches will accelerate in the coming year. One notable example is the expanding use of artificial intelligence (AI) in education. AI-powered tutoring systems can provide personalized feedback and support to students, adapting to their individual learning styles and needs. Furthermore, virtual and augmented reality technologies are poised to transform the learning experience, offering immersive and engaging simulations that can enhance comprehension and retention.
Consider, for instance, the use of VR to simulate historical events or scientific experiments, providing students with a far more interactive and memorable learning experience than traditional methods. Another significant trend is the growing emphasis on project-based learning, where students engage in collaborative projects that require them to apply their knowledge and skills to real-world problems. This approach fosters critical thinking, problem-solving, and teamwork skills, crucial for success in the 21st-century workforce.
Finally, the integration of maker spaces and hands-on learning opportunities will continue to gain traction, providing students with the opportunity to design, build, and create, further developing their creativity and innovation skills.
Global Connectivity

The period between 2030 and 2040 will witness a transformative shift in global connectivity, driven by technological advancements, evolving infrastructure, and shifting geopolitical landscapes. Predicting the precise state of global connectivity requires considering diverse factors, including economic development, government regulations, and societal acceptance of new technologies. This analysis will explore anticipated trends, potential challenges and opportunities, and the impact on various sectors, ultimately outlining plausible scenarios for the future of global connectivity.
Anticipated State of Global Connectivity (2030-2040)
By 2030-2040, global internet penetration will likely surpass 80%, although the distribution will remain uneven. North America and Europe will maintain high broadband access rates (over 95%), driven by robust infrastructure and high disposable incomes. Asia will experience significant growth, with expanding broadband access, particularly in urban areas, though rural penetration may lag. Africa and South America will see considerable improvements, but substantial digital divides will persist due to infrastructure limitations and affordability issues.
Oceania, with its diverse geography, will show a mixed picture, with high connectivity in urban centers and lower rates in remote areas. Average internet speeds will increase significantly globally, with the adoption of 5G and 6G technologies, although disparities in access will likely lead to a considerable gap in speed between developed and developing nations. Government policies promoting digital inclusion will play a crucial role in bridging this gap, alongside substantial investment in infrastructure development and initiatives to reduce the cost of internet access.
For example, initiatives like the expansion of fiber optic networks and satellite internet services will significantly improve access in underserved areas.
Challenges and Opportunities Related to Global Connectivity (2030-2040)
The expansion of global connectivity presents both significant challenges and opportunities. Addressing these challenges requires proactive strategies and international cooperation.
| Challenge | Opportunity | Mitigation Strategy/Actionable Item |
|---|---|---|
| Digital Divide | Increased economic productivity | Targeted infrastructure investment in underserved areas; subsidized internet access programs; development of affordable technologies |
| Cybersecurity Threats | Development of new communication technologies | Enhanced cybersecurity protocols; international collaboration on cybersecurity standards; investment in cybersecurity education and training |
| Data Privacy Concerns | Global collaboration and knowledge sharing | Robust data privacy regulations; ethical guidelines for data collection and use; promotion of data literacy |
| Infrastructure Limitations | Improved access to education and healthcare | Public-private partnerships for infrastructure development; investment in resilient infrastructure; development of innovative infrastructure solutions |
| Regulatory Barriers | Creation of new markets and business opportunities | Streamlined regulatory frameworks; international cooperation on regulatory harmonization; fostering innovation-friendly policies |
Impact of Advancements in Connectivity on Various Sectors (2030-2040)
Advancements in connectivity will profoundly impact various sectors.
Healthcare
Telemedicine will become increasingly prevalent, enabling remote consultations, diagnosis, and monitoring. Remote patient monitoring devices will allow for proactive healthcare management, reducing hospital readmissions and improving patient outcomes. For example, wearable sensors tracking vital signs will transmit data directly to healthcare providers, enabling early intervention for chronic conditions. This increased access to care, particularly in rural and underserved areas, will improve health outcomes and reduce healthcare costs in the long run.
Planning your year ahead? The period from June 2024 to June 2025 encompasses a significant timeframe for many, including West Virginia University students. For those seeking specific dates, consult the official wvu 2024-2025 academic calendar to ensure alignment with important academic milestones. Returning to the broader June 2024 to June 2025 calendar, remember to factor in personal and professional commitments alongside those key academic dates.
Education
Online learning platforms will become more sophisticated, offering personalized learning experiences tailored to individual student needs. Access to educational resources will be democratized, with students globally able to access high-quality educational materials regardless of their location. Examples include AI-powered tutoring systems and virtual reality educational experiences, enhancing engagement and knowledge retention. The increased accessibility of education will contribute to a more skilled and knowledgeable workforce globally.
Agriculture
Precision agriculture, utilizing IoT sensors and data analytics, will optimize resource use, increasing crop yields and reducing environmental impact. Smart irrigation systems, using real-time data on soil moisture and weather conditions, will minimize water waste. Drone technology will enable efficient monitoring of crops, enabling early detection of pests and diseases. This increased efficiency and sustainability will enhance food security and contribute to a more environmentally friendly agricultural sector.
Geopolitical Implications of Varying Levels of Global Connectivity
Uneven global connectivity will exacerbate existing geopolitical disparities. Regions with superior connectivity will enjoy economic advantages, potentially leading to increased influence in international affairs. Conversely, regions with limited access may face marginalization and instability, potentially creating new sources of conflict. The digital divide could further deepen existing inequalities, impacting social stability and international relations. The control and regulation of critical digital infrastructure will become a major point of contention, influencing power dynamics on a global scale.
Scenarios for Global Connectivity in 2040
Three distinct scenarios illustrate the potential trajectories of global connectivity in 2040:
Optimistic Scenario
Widespread access to high-speed internet, driven by substantial investments in infrastructure and policies promoting digital inclusion. This scenario results in increased economic growth, improved healthcare outcomes, and enhanced educational opportunities globally. Key drivers include massive public and private investment in infrastructure, technological breakthroughs, and international cooperation.
Pessimistic Scenario
A significant digital divide persists, with limited access to internet and technology in many parts of the world. This scenario leads to increased inequality, social unrest, and limited economic growth in underserved regions. Key drivers include lack of investment in infrastructure, political instability, and technological monopolies.
Realistic Scenario
A blend of progress and challenges, with significant improvements in connectivity but persistent disparities between regions. This scenario leads to uneven economic growth and varying levels of access to healthcare and education, requiring continued efforts to bridge the digital divide. Key drivers include a combination of positive and negative factors, leading to a more nuanced outcome.
Executive Summary
Global connectivity in 2030-2040 presents both immense opportunities and significant challenges. While technological advancements promise increased access and economic growth, the digital divide, cybersecurity threats, and data privacy concerns remain significant hurdles. Bridging the digital divide requires targeted investments in infrastructure, affordable technologies, and supportive government policies. International cooperation is crucial to address cybersecurity threats and establish robust data privacy regulations.
The uneven distribution of connectivity will have profound geopolitical implications, influencing economic power dynamics and social stability. The future of global connectivity will depend on proactive strategies, international collaboration, and a commitment to inclusive and equitable access to technology.
Space Exploration and Discoveries
The period from June 2024 to June 2025 promises to be a significant one for space exploration, building upon decades of research and technological advancements. We can anticipate a flurry of activity, from continued exploration of Mars to deeper probes into the mysteries of our solar system and beyond. The data gathered will undoubtedly reshape our understanding of planetary formation, the search for extraterrestrial life, and the very nature of the universe.The advancements in space exploration during this timeframe will significantly impact our understanding of the universe by providing unprecedented access to data and observations.
This data will allow scientists to refine existing theories and formulate new hypotheses, potentially leading to revolutionary breakthroughs in our understanding of cosmology, astrophysics, and planetary science.
Artemis Program Progress
The Artemis program, aiming for a sustained human presence on the Moon, will continue its crucial phases during this period. We can expect further progress in the development and testing of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and the Orion spacecraft. Successful missions will focus on establishing a lunar base camp, testing technologies for resource utilization on the Moon, and conducting scientific research in the lunar environment.
This includes collecting samples from previously unexplored regions and conducting detailed geological surveys. The data collected will inform future missions to Mars and other celestial bodies.
Mars Exploration Initiatives
Several robotic missions are planned or ongoing to Mars during this timeframe. The Perseverance rover will continue its search for signs of past microbial life, collecting samples for future return to Earth. Other missions might involve deploying new landers or orbiters to study the Martian atmosphere, geology, and potential subsurface water resources. The cumulative data from these missions will paint a more comprehensive picture of Mars’ history and potential for habitability.
For example, the analysis of subsurface ice deposits could provide crucial insights into the availability of water resources for future human missions.
James Webb Space Telescope Discoveries
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), already revolutionizing our view of the cosmos, will continue its observations, potentially unveiling further details about the early universe, distant galaxies, and exoplanetary systems. We can anticipate discoveries related to the formation of stars and planets, the characterization of exoplanetary atmospheres, and the detection of biosignatures on potentially habitable planets. The JWST’s unparalleled sensitivity will allow scientists to probe deeper into the universe than ever before, providing crucial data for refining cosmological models and understanding the evolution of galaxies.
For instance, detailed spectroscopic analysis of exoplanet atmospheres might reveal the presence of molecules indicative of life.
Private Sector Space Initiatives
Private companies are playing an increasingly important role in space exploration. During this period, we can expect continued advancements in reusable launch systems, satellite constellations, and commercial space tourism. These initiatives will not only drive down the cost of access to space but also foster innovation and collaboration, leading to faster progress in scientific discovery. For example, SpaceX’s Starship program aims to create a fully reusable spacecraft capable of transporting large payloads to the Moon and Mars, potentially revolutionizing space transportation.
Question Bank
What are some effective ways to handle scheduling conflicts arising from recurring events?
Prioritize tasks and appointments based on importance and deadlines. Utilize buffer time between events to accommodate unforeseen delays. Consider flexible scheduling methods if possible, and communicate proactively with others involved in the scheduling to find mutually agreeable solutions.
How can I adapt the personal scheduling strategies presented to my specific needs?
Analyze your own working style, preferences, and typical daily/weekly routines. Select the strategy that best aligns with your personality type and adapt the calendar features (color-coding, tagging, etc.) to match your individual needs and priorities. Experiment with different approaches until you find the optimal balance between structure and flexibility.
Where can I find reliable sources for economic forecasts and global event predictions?
Reputable sources for economic forecasts include the International Monetary Fund (IMF), the World Bank, and the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). For global event predictions, consult established news organizations like the Associated Press, Reuters, and BBC News, as well as reputable think tanks and academic institutions.
