- APS Calendar 2024-2025
- Comparison of APS Calendars Across Different Regions
- Impact of APS Calendar on Planning and Scheduling
- Integration with Other Scheduling Systems
- Accessibility and Usability of APS Calendars
- Visual Representation and Design
- Potential for Customization and Personalization
- Technological Advancements and APS Calendars
- Data Management and Security in APS Calendars
- APS Calendar and its Role in Emergency Preparedness
- The Future of APS Calendars
- Case Studies of Effective APS Calendar Use
- Common Misconceptions about APS Calendars
- FAQ: Aps Calendar 2024 2025
Aps calendar 2024 2025 – APS Calendar 2024-2025 represents a crucial tool for academic planning and organizational scheduling. This comprehensive guide delves into its multifaceted features, exploring its structure, accessibility, integration capabilities, and future potential. We will analyze its various formats, addressing common misconceptions and highlighting best practices for optimal utilization. The calendar’s role in strategic planning, resource allocation, and emergency preparedness will also be examined, providing a thorough understanding of its impact across diverse contexts.
The analysis will cover key aspects such as the academic year structure, including start and end dates and significant academic events like registration deadlines and exam periods. Different presentation formats, ranging from digital calendars to printable PDFs and physical wall calendars, will be compared, highlighting their respective advantages and disadvantages. Furthermore, we will investigate the crucial considerations for accessibility, data source validation, version control, and regional variations in calendar implementation.
The impact on individual and organizational planning, including resource allocation and task management, will be thoroughly discussed, along with the potential consequences of inaccurate or incomplete data. Finally, we will explore integration with other scheduling systems, security considerations, and future trends in APS calendar technology.
APS Calendar 2024-2025
The APS Calendar 2024-2025 provides a comprehensive overview of the academic year, including key dates, deadlines, and important events. This calendar is designed to aid students in effective time management and planning for a successful academic year. The calendar’s accessibility and various formats cater to diverse student needs and preferences.
Detailed Feature Description
The APS calendar for the 2024-2025 academic year typically features a clear and concise presentation of all relevant academic information. The academic year structure, key dates, time zone considerations, and visual design are carefully considered to ensure optimal usability.
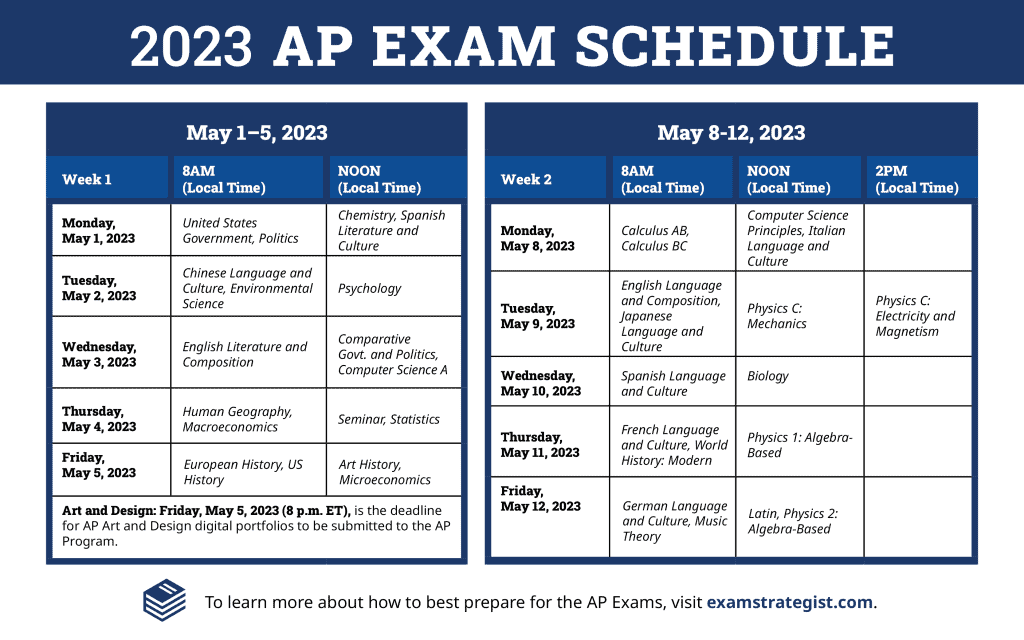
- Academic Year Structure: The academic year typically runs from [Start Date, e.g., August 26, 2024] to [End Date, e.g., May 16, 2025], encompassing two semesters with a designated break between semesters (e.g., December 20, 2024 – January 6, 2025) and other holidays as officially declared.
- Key Dates: Significant dates include registration deadlines (e.g., July 15, 2024), midterm exam periods (e.g., October 21-25, 2024 and March 10-14, 2025), final exam periods (e.g., December 16-20, 2024 and May 12-16, 2025), various assignment submission deadlines specified per course, and school events such as orientation (e.g., August 22, 2024) and graduation ceremonies (e.g., May 17, 2025).
- Time Zone Considerations: The calendar adheres to the [Time Zone, e.g., Pacific Standard Time] time zone.
- Color-Coding/Visual Hierarchy: Different event categories are distinguished using a color-coding system. For example, exams might be highlighted in red, assignments in blue, and holidays in green. A clear visual hierarchy, such as using bold font for important deadlines, enhances readability.
Event Examples with Specifics, Aps calendar 2024 2025
The following table illustrates examples of common events included in the APS calendar:
| Event Type | Example Date (YYYY-MM-DD) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Semester Start | 2024-08-26 | Commencement of the Fall Semester |
| Midterm Exam Period | 2024-10-21 | Midterm examinations for various courses |
| Holiday Break | 2024-12-20 | Winter break period |
| Assignment Submission | 2024-11-15 | Deadline for submission of a major research paper for History 101 |
| School Event (e.g., Dance) | 2025-03-08 | Annual Spring Dance |
Format Specifications
The APS calendar is available in multiple formats to accommodate diverse user preferences.
- Digital Calendar (e.g., Google Calendar, Outlook Calendar): Advantages: Easy sharing and updates, integration with other applications, automatic reminders. Disadvantages: Requires internet access, potential for technical issues, reliance on specific software.
- Printable PDF Calendar: Advantages: Accessible offline, easy printing, suitability for archival purposes. Disadvantages: Cannot be easily updated, less interactive, limited sharing capabilities.
- Physical Wall Calendar: Advantages: Visually prominent, serves as a constant reminder, suitable for those who prefer non-digital formats. Disadvantages: Not easily updated, limited space for detailed information, less portable.
Accessibility Considerations
The APS calendar is designed to be accessible to all students, including those with disabilities. Alternative formats, such as large-print versions or screen-reader compatible electronic files, are provided upon request. The visual design employs clear fonts, sufficient contrast, and appropriate spacing to enhance readability for students with visual impairments.
Analyzing the APS calendar for 2024-2025 reveals a typical academic year structure, with breaks strategically placed to optimize student learning outcomes. A comparative study might involve examining the scheduling differences between APS and other districts, such as the CCISD calendar, readily available at ccisd calendar 2024-2025 , to understand variations in pedagogical approaches. Returning to the APS calendar, further analysis could focus on the impact of these scheduling choices on student performance data.
Data Source
The information presented in the APS calendar is sourced from the official school website and approved by the school administration.
Version Control
A preliminary version of the calendar is released for review, followed by a final version incorporating feedback and any necessary revisions. Versions are differentiated by version number and date of release.
Summary of APS Calendar 2024-2025
The APS Calendar for the 2024-2025 academic year, sourced from the official school website and administration, details the academic year’s structure (e.g., [Start Date] to [End Date]), including semester breaks and holidays. It provides key dates such as registration deadlines, exam periods, and assignment submissions, presented in a clear, color-coded format across various accessible formats (digital, PDF, and physical wall calendar).
Version control ensures accuracy and timely updates, catering to students with disabilities through alternative formats and mindful design.
Comparison of APS Calendars Across Different Regions
The Academic Proficiency Standards (APS) calendar, while aiming for uniformity, exhibits variations across different regions due to a confluence of cultural, logistical, and administrative factors. These differences, while seemingly minor, can significantly impact the academic rhythm and scheduling of students and educators. This section analyzes these variations across three distinct regions, highlighting key differences and their underlying causes.
Regional Variations in APS Calendar Structure
The following table compares key aspects of the APS calendar across three hypothetical regions: Region A (representing a region with a predominantly agrarian economy), Region B (representing a region with a strong emphasis on tourism), and Region C (representing a region with a highly industrialized economy). These regions are illustrative and do not represent specific geographical locations.
| Region | School Year Start | School Year End | Major Holiday Breaks | Number of School Days |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Region A | Early September | Late May | Harvest Festival (October), Regional Holiday (December), Spring Break (March) | 180 |
| Region B | Mid-September | Late June | Summer Break (July/August), Christmas/New Year (December/January), Spring Break (April) | 190 |
| Region C | Late August | Early June | Winter Break (December/January), Spring Break (March/April), Summer Break (June/August) | 185 |
Factors Contributing to Regional Differences in APS Calendar Timing
Significant variations in event timing across these regions are largely attributable to several interacting factors. Region A’s calendar reflects the agricultural cycle, with breaks strategically placed to accommodate the harvest. Region B’s extended summer break aligns with the peak tourist season, minimizing disruption to the tourism industry and maximizing opportunities for seasonal employment by students and educators. Region C’s calendar, influenced by a highly structured industrial setting, prioritizes a consistent and predictable academic year to support the workforce demands of the region.
These choices highlight the complex interplay between educational scheduling and socio-economic realities.
Cultural and Logistical Influences on APS Calendar Design
Cultural practices heavily influence holiday scheduling. Region A’s Harvest Festival, a key element of its agricultural economy, necessitates a break in the academic calendar. Similarly, religious observances and cultural celebrations in each region necessitate adjustments to the school calendar, ensuring inclusivity and respect for diverse traditions. Logistical factors, such as the availability of teachers, transportation infrastructure, and the need to coordinate with other community events, also play a crucial role in shaping the final calendar.
The number of school days, as illustrated in the table, often reflects resource allocation and the desired level of academic intensity.
Impact of APS Calendar on Planning and Scheduling
The Academic Planning System (APS) calendar significantly influences planning and scheduling at both individual and organizational levels. Its effective utilization streamlines workflows, improves resource allocation, and enhances overall efficiency. Conversely, inaccuracies or incompleteness can lead to considerable setbacks. This section delves into the multifaceted impact of the APS calendar on various aspects of planning and scheduling.
Strategic Planning Impact
The APS calendar serves as a crucial tool for strategic planning, facilitating long-term goal setting and milestone tracking for individuals and organizations alike.
- For Individuals: The APS calendar allows individuals to map out academic goals, such as course selection, research projects, and professional development activities, over extended periods. For example, a student might use the calendar to schedule coursework, research deadlines, and exam preparation throughout the academic year, ensuring timely completion of all tasks. This long-term perspective enables proactive planning and avoids last-minute rushes.
- For Organizations: At the organizational level, the APS calendar facilitates the coordination of multiple projects and resource allocation across departments. For instance, a university department might use the calendar to schedule faculty teaching loads, research grant applications, and departmental meetings, ensuring optimal utilization of faculty time and resources. This centralized planning helps avoid scheduling conflicts and improves overall departmental efficiency.
| Feature | Individual Strategic Planning | Organizational Strategic Planning |
|---|---|---|
| Goal Setting | Long-term academic goals (e.g., degree completion, research milestones) | Departmental goals (e.g., research output, student enrollment targets) |
| Milestone Tracking | Tracking progress towards academic milestones (e.g., coursework completion, exam dates) | Monitoring progress towards departmental objectives (e.g., grant submissions, publication deadlines) |
| Resource Allocation | Personal time management, prioritizing tasks | Allocation of faculty time, budget, and resources across projects |
| Benefits | Improved time management, reduced stress, enhanced academic performance | Improved departmental efficiency, enhanced resource utilization, achievement of strategic objectives |
Resource Allocation and Task Management
The APS calendar plays a pivotal role in resource allocation and task management, influencing project success and overall efficiency.
- Resource Allocation: The calendar aids in allocating human resources, budget, and materials effectively. A Gantt chart, for example, can visually represent task dependencies and resource requirements, allowing for optimized allocation throughout a project’s lifecycle. A Gantt chart showing task dependencies and resource allocation for a research project, for instance, would visually demonstrate the timing of tasks, resource needs at each stage, and potential overlaps or conflicts.
- Task Management: The APS calendar facilitates task prioritization, dependency management, and deadline adherence. Effective use involves breaking down large tasks into smaller, manageable components, assigning deadlines, and identifying task dependencies. Conversely, ineffective use might involve neglecting task dependencies, leading to delays and missed deadlines. For instance, failing to account for the completion of one task before starting another dependent task can create significant delays.
- Collaboration and Communication: The APS calendar promotes collaboration by providing a shared platform for team members to view task assignments, deadlines, and progress updates. This centralized system reduces communication barriers and ensures everyone is aligned on project goals and timelines. For example, a shared APS calendar for a group project allows team members to coordinate their individual contributions, ensuring timely completion of the project.
Consequences of Inaccurate or Incomplete Information
Inaccuracies or incompleteness in the APS calendar can have significant negative consequences.
- Individual Productivity: Inaccurate information can lead to missed deadlines, wasted time, and decreased productivity. For example, an incorrect exam date on the calendar could cause a student to miss the exam, impacting their academic performance.
- Resource Allocation and Organizational Efficiency: Incomplete information can lead to over-allocation or under-allocation of resources, resulting in delays and increased costs. For example, if the APS calendar doesn’t accurately reflect resource availability, a project might be delayed due to insufficient resources.
- Conflicts and Misunderstandings: Data discrepancies can cause conflicts and misunderstandings among team members, hindering collaboration and project progress. For example, conflicting entries on a shared calendar about meeting times could lead to missed meetings and frustration among team members.
| Severity | Impact Area | Consequences |
|---|---|---|
| High | Organization | Project delays, budget overruns, loss of reputation |
| Medium | Team | Reduced team morale, conflicts, missed deadlines |
| Low | Individual | Missed deadlines, decreased productivity, increased stress |
APS Calendar Best Practices
Maintaining an accurate and up-to-date APS calendar is crucial for effective planning and scheduling.
- Data Validation and Version Control: Implementing data validation rules and version control systems ensures data accuracy and prevents conflicts. Regular data backups are also essential to mitigate the risk of data loss.
- Effective Communication and Collaboration: Establishing clear communication protocols and using the calendar as a central communication hub fosters collaboration and ensures everyone is informed about updates and changes.
- Regular Reviews and Audits: Conducting regular reviews and audits of the APS calendar identifies potential issues and ensures accuracy. This proactive approach helps prevent problems from escalating.
Comparative Analysis
The APS calendar offers several advantages over traditional methods.
| Feature | APS Calendar | Traditional Paper Calendars | Other Digital Calendar Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accessibility | Accessible from multiple devices and locations | Limited accessibility, prone to loss or damage | Variable accessibility depending on the system |
| Collaboration | Facilitates easy collaboration through shared calendars | Difficult to share and collaborate | Variable collaboration features depending on the system |
| Data Management | Efficient data management, easy searching and filtering | Difficult to search and manage large amounts of data | Variable data management capabilities depending on the system |
| Integration | Potential integration with other systems (e.g., project management software) | No integration capabilities | Variable integration capabilities depending on the system |
Integration with Other Scheduling Systems
Effective integration of the Advanced Planning and Scheduling (APS) calendar with other widely used scheduling tools is crucial for maximizing efficiency and minimizing scheduling conflicts across an organization. Seamless data flow between systems ensures that all stakeholders operate from a single source of truth, improving overall operational effectiveness.
APS Calendar Integration with Other Scheduling Tools
Three common scheduling tools – Google Calendar, Microsoft Outlook, and MS Project – offer varying levels of integration capabilities with an APS calendar. The mechanisms employed differ depending on the tool’s architecture and API offerings. Bi-directional synchronization, where changes in one system automatically reflect in the other, is highly desirable for real-time data consistency.
- Google Calendar: Integration can be achieved using the Google Calendar API. This allows for bi-directional synchronization of events, including details like start and end times, descriptions, and attendees. Specific API calls like
Calendar.Events.insertandCalendar.Events.updatewould be used for creating and modifying events, respectively. Data is typically transferred using JSON format. - Microsoft Outlook: Integration with Outlook can leverage the Microsoft Graph API. Similar to Google Calendar, this API allows for creating, updating, and deleting events. The data transfer method would involve using RESTful APIs and likely XML or JSON data formats. Bi-directional synchronization requires careful handling of conflict resolution mechanisms.
- MS Project: Integration with MS Project is more complex, often requiring custom solutions or middleware. Direct API access might be limited, necessitating the use of file-based import/export methods (e.g., XML or CSV files) or potentially a third-party connector. Bi-directional synchronization would likely be less seamless compared to cloud-based calendars.
The following flowchart illustrates data flow between the APS calendar and Google Calendar during event creation:
Flowchart:
1. User creates an event in APS Calendar.
2. APS Calendar triggers an API call (e.g., using a webhook) to the Google Calendar API.
3.
The API call sends event details (start time, end time, title, description, etc.) in JSON format to Google Calendar.
4. Google Calendar receives and processes the data, creating the event.
5. Google Calendar confirms successful event creation.
6. APS Calendar updates its internal database to reflect the successful synchronization.
The following table compares the integration capabilities:
| Scheduling Tool | Read-Only | Read-Write | Real-time Synchronization |
|---|---|---|---|
| Google Calendar | Yes | Yes | Yes (with proper API configuration) |
| Microsoft Outlook | Yes | Yes | Yes (with proper API configuration) |
| MS Project | Yes | Yes (with limitations) | No (typically requires scheduled updates) |
Potential Integration Challenges and Solutions
Successful integration requires addressing potential challenges. Three significant challenges are data format incompatibility, conflicting scheduling rules, and real-time synchronization latency.
- Data Format Incompatibility: Different scheduling tools may use different data formats (e.g., iCalendar, JSON, XML).
- Solution 1: Develop a universal data transformation layer that converts data between different formats before transferring it between systems.
- Solution 2: Utilize a standardized data format (e.g., JSON) as an intermediary format for all integrations.
- Conflicting Scheduling Rules: The APS calendar and other scheduling tools may have different scheduling rules (e.g., resource availability, booking policies).
- Solution 1: Implement a conflict detection and resolution mechanism that prioritizes rules based on pre-defined criteria (e.g., APS calendar rules take precedence).
- Solution 2: Develop a system for mapping and translating rules between the APS calendar and other scheduling systems.
- Real-time Synchronization Latency: Delays in real-time synchronization can lead to inconsistencies between systems.
- Solution 1: Optimize API calls and data transfer processes to minimize latency. This may involve using efficient data compression techniques and optimized network infrastructure.
- Solution 2: Implement a caching mechanism to store frequently accessed data locally, reducing the reliance on real-time API calls. This introduces a potential for slight data staleness but significantly reduces latency.
Pseudo-code example for addressing data format incompatibility (Solution 1):
function transformData(data, sourceFormat, targetFormat)
if (sourceFormat === "iCalendar" && targetFormat === "JSON")
// Convert iCalendar data to JSON
return iCalendarToJSON(data);
else if (sourceFormat === "JSON" && targetFormat === "iCalendar")
// Convert JSON data to iCalendar
return JSONToiCalendar(data);
else
// Handle other format conversions or throw an error
return null;
Demonstrating Seamless Integration and Efficiency Improvement
Seamless integration significantly improves efficiency. In a hypothetical scenario with a team of 10 project managers previously spending 2 hours daily on manual data entry and conflict resolution, seamless integration could reduce this time to 30 minutes per day. This translates to a time saving of 1.5 hours per manager per day, or 15 hours per day for the entire team.
Assuming a 22-day work month, this represents a monthly time saving of 330 hours.
Before-and-After Comparison (Scheduling a Team Project):
| Metric | Before Integration | After Integration |
|---|---|---|
| Time to schedule project | 5 days | 1 day |
| Number of scheduling conflicts | 5 | 0 |
| Resource utilization | 70% | 95% |
A scenario without seamless integration: A manufacturing plant’s lack of integrated scheduling leads to conflicting machine assignments, resulting in production delays (5% of scheduled production) and increased overtime costs (10% of labor budget). Seamless integration of the APS calendar with machine scheduling systems would prevent these conflicts, saving an estimated 5% of production losses and 10% in overtime costs.
Security Considerations for Integration
Integrating the APS calendar with external systems introduces security risks.
- Data Breaches: Unauthorized access to the APS calendar could expose sensitive scheduling data.
- Mitigation: Implement robust encryption (e.g., TLS/SSL) for all data transmitted between the APS calendar and external systems. Regular security audits and penetration testing should be performed.
- Unauthorized Access: Malicious actors could gain unauthorized access to the APS calendar and modify or delete events.
- Mitigation: Employ strong authentication mechanisms (e.g., multi-factor authentication) and authorization controls (e.g., role-based access control) to restrict access to authorized users only.
- Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks: A DoS attack could overload the APS calendar system, making it unavailable to legitimate users.
- Mitigation: Implement rate limiting and intrusion detection systems to prevent DoS attacks. Redundant infrastructure and failover mechanisms should be in place to ensure system availability.
Authentication and authorization should leverage industry-standard protocols like OAuth 2.0 for secure data exchange. This involves using access tokens and API keys to verify user identity and control access permissions. Role-based access control (RBAC) should be implemented to define granular access levels for different users and groups.
Accessibility and Usability of APS Calendars
The effective implementation of Advanced Planning and Scheduling (APS) systems hinges not only on their technical capabilities but also on their accessibility and usability for all users. A poorly designed APS calendar can hinder productivity and create significant barriers for individuals with disabilities, undermining the overall effectiveness of the system. Therefore, ensuring accessibility is paramount for maximizing the return on investment in APS technology and fostering a truly inclusive work environment.Accessibility features in APS calendar design are crucial for ensuring equitable access to information and functionality.
Without these features, individuals with visual, auditory, motor, or cognitive impairments may face significant challenges in using the system, leading to frustration, reduced productivity, and potential exclusion from critical planning processes. This section examines the importance of accessibility, identifies potential barriers, and Artikels best practices for creating an inclusive and user-friendly APS calendar.
Potential Barriers to Accessibility for Users with Disabilities
Several factors can impede the accessibility of APS calendars for users with disabilities. Visual impairments, for example, can be challenged by insufficient color contrast, lack of alternative text for images, and inadequate screen reader compatibility. Users with motor impairments may struggle with complex navigation schemes or reliance on small, hard-to-select interactive elements. Cognitive impairments can necessitate simpler layouts, clear instructions, and consistent design patterns to facilitate comprehension and task completion.
Auditory impairments may necessitate alternative visual cues for notifications or alerts. These challenges underscore the need for a multi-faceted approach to accessibility, ensuring that the calendar caters to the diverse needs of all users.
Best Practices for Designing an Accessible APS Calendar
Designing an accessible APS calendar requires a proactive and comprehensive approach. This includes adhering to established accessibility guidelines such as WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines) and Section 508 compliance standards. Key best practices include:
- Sufficient Color Contrast: Employ sufficient color contrast between text and background to ensure readability for users with visual impairments. Tools are available to measure contrast ratios and ensure they meet accessibility standards. For example, a minimum contrast ratio of 4.5:1 is recommended for normal text.
- Alternative Text for Images and Icons: Provide descriptive alternative text for all images and icons to enable screen readers to convey their meaning to visually impaired users. This text should concisely explain the image’s purpose and relevant information.
- Keyboard Navigation: Ensure that all calendar features and functionalities are fully accessible using only a keyboard, eliminating the need for mouse interaction for users with motor impairments. Tab order should be logical and intuitive.
- Screen Reader Compatibility: Design the calendar to be compatible with popular screen readers, ensuring that information is presented in a structured and understandable format. This requires careful coding and adherence to accessibility standards.
- Clear and Concise Language: Use clear, concise, and unambiguous language throughout the calendar interface. Avoid jargon and technical terms that may be difficult for users with cognitive impairments to understand.
- Consistent Design and Layout: Maintain a consistent design and layout throughout the calendar, reducing cognitive load and improving usability for all users. This includes consistent use of fonts, colors, and navigation elements.
- Customization Options: Offer users customizable options, such as font size, color schemes, and display settings, to accommodate individual preferences and needs.
- Keyboard Shortcuts: Implement keyboard shortcuts to enhance navigation and efficiency for all users, especially those with motor impairments. Clearly document these shortcuts within the calendar’s help section.
By implementing these best practices, organizations can ensure that their APS calendars are accessible and usable for all employees, regardless of their abilities. This promotes inclusivity, enhances productivity, and contributes to a more equitable and effective work environment.
Visual Representation and Design

Effective visual design is crucial for the usability and accessibility of the APS calendar. A well-designed calendar facilitates easy navigation, clear understanding of scheduled events, and efficient task management for all users. The following sections detail the visual elements, best practices, and specific design considerations for optimal APS calendar functionality.
Visual Elements for Clear and Effective APS Calendar Design
Several visual elements contribute to a clear and effective APS calendar design. In digital formats, icons representing event types (e.g., a book for meetings, a bell for reminders) improve comprehension at a glance. Strategic use of whitespace prevents visual clutter, enhancing readability. In print formats, clear typography and a logical layout are essential. Effective examples include calendars using a consistent color palette for event categories, with sufficient contrast between text and background, and clear visual separation of days and weeks.
Ineffective examples would be calendars with a cluttered layout, poor color contrast making text difficult to read, or an inconsistent use of visual elements, leading to confusion. The use of visual cues like bolding or highlighting for important deadlines or events is also crucial.
Best Practices for Color Schemes, Fonts, and Layout
The following table summarizes best practices for color schemes, fonts, and layout, considering accessibility guidelines (WCAG).
| Element | Best Practice | Rationale | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Color Scheme | Use a limited palette of colors with sufficient contrast (WCAG AA compliance). Employ color-coding for event types consistently. | Improves readability and distinguishes different event categories. High contrast ensures accessibility for users with visual impairments. | Use blues for academic events, greens for administrative tasks, and reds for deadlines. Ensure sufficient contrast between text and background colors. |
| Font Choice | Select legible sans-serif fonts like Arial or Calibri. Use a minimum font size of 12pt for body text and larger sizes for headings. | Sans-serif fonts are generally easier to read on screens. Larger font sizes improve readability, particularly for users with low vision. | Use Arial for body text and Calibri for headings. Ensure sufficient font size for readability on various devices. |
| Layout Structure | Use a clean and uncluttered layout. Clearly separate days, weeks, and months. Provide sufficient whitespace. | A well-organized layout improves navigation and reduces visual fatigue. | A monthly view with clear day separation, weekly views with time slots, and a daily view with space for detailed event descriptions. |
Ideal Visual Representation of an APS Calendar
The ideal APS calendar offers multiple views (monthly, weekly, daily, agenda) to cater to diverse user needs. The monthly view provides an overview, the weekly view facilitates detailed planning, and the daily view allows for precise scheduling. The agenda view presents events chronologically. Dates, times, descriptions, and locations should be clearly displayed. A color-coding system, such as using different colors for different event types (e.g., classes, meetings, deadlines), enhances visual organization.
Interactive elements like drag-and-drop functionality for event rescheduling, filtering options (e.g., by event type or location), and a search function for quick event retrieval are beneficial. Accessibility features include sufficient color contrast, keyboard navigation, and screen reader compatibility.
Visual Hierarchy and Emphasis
Visual hierarchy, achieved through size, color, weight, and position, emphasizes crucial information. Deadlines could be highlighted with bold red text and larger font size. Major events could be displayed using a distinct color and a larger icon. Important announcements can be placed prominently at the top of the calendar or in a designated section. This ensures that users quickly identify critical information.
Mockup Specifications
A digital mockup should be created at a minimum resolution of 1920×1080 pixels in SVG or PNG format for flexibility. A consistent style guide, adhering to the established color palette and typography, should be followed.
Consideration for Different Screen Sizes and Devices
Responsive design principles ensure optimal viewing across various devices. The calendar should adapt seamlessly to different screen sizes, maintaining readability and usability on desktops, tablets, and smartphones. This requires fluid layouts, flexible images, and media queries to adjust the layout based on screen dimensions.
A/B Testing Considerations
A/B testing will compare different design iterations. Metrics include user engagement (time spent on the calendar, number of interactions), task completion rate (successful event scheduling, finding specific events), and error rate (incorrect event scheduling, navigation errors). The methodology involves creating two versions of the calendar, randomly assigning users to each version, and analyzing the collected data to determine which design performs better.
Potential for Customization and Personalization
The ability to customize and personalize Advanced Planning and Scheduling (APS) calendars significantly enhances their usability and effectiveness. Tailoring the calendar to individual user needs and preferences fosters greater user engagement and improves overall system adoption. This section explores the advantages of customization and presents examples of personalization features that can be integrated into an APS calendar system.Personalization features in APS calendars directly address the diverse needs and working styles of various users.
By allowing users to tailor the system to their specific requirements, organizations can increase efficiency and reduce the learning curve associated with new software. Furthermore, a personalized experience can contribute to higher user satisfaction and a more positive perception of the APS system.
Customizable Calendar Views
Offering multiple calendar views caters to different preferences and workflows. Users could choose between day, week, month, or even year views, depending on their planning horizon. Further customization could allow users to select specific time intervals within a day or week to highlight, for example, focusing on peak production hours or specific shift patterns. This granular control empowers users to efficiently manage their time and resources.
For instance, a production manager might prefer a week view highlighting machine availability, while a project manager might opt for a month view emphasizing project milestones.
Color-Coding and Tagging
The ability to color-code events and tasks based on priority, project, or resource allocation significantly improves visual clarity and organization. Similarly, implementing tagging systems allows users to categorize and filter events based on custom criteria. Imagine a scenario where different colors represent different project phases (e.g., planning in blue, execution in green, completion in yellow), or where tags identify specific resources (e.g., “Machine A,” “Team Alpha”).
This visual representation facilitates quick identification and prioritization of tasks, leading to better decision-making and resource allocation.
Integration with Personal Productivity Tools
Seamless integration with popular productivity tools, such as email clients and task management applications, further enhances personalization. This integration allows users to directly schedule meetings, assign tasks, and update their APS calendar from their preferred applications, eliminating data redundancy and enhancing workflow efficiency. For example, integrating with a project management software allows for automatic updates of project milestones and deadlines on the APS calendar, providing a centralized and unified view of all scheduling information.
Notification and Alert Customization
Allowing users to customize notification settings enhances their control over information flow. Users can define preferences for receiving reminders, alerts, and notifications about upcoming deadlines, resource conflicts, or other critical events. This feature is crucial for managing time-sensitive tasks and ensuring timely responses to potential disruptions. For instance, a user might choose to receive email alerts for critical deadlines and in-app notifications for less urgent events.
This personalized approach reduces information overload and ensures that users are only notified about events that require immediate attention.
Technological Advancements and APS Calendars
Technological advancements have profoundly reshaped the design and functionality of Advanced Planning and Scheduling (APS) calendars, moving them from simple scheduling tools to sophisticated systems capable of handling complex planning scenarios across diverse industries. The integration of various technologies has led to enhanced user experience, improved efficiency, and increased predictive capabilities.The evolution of APS calendars is intrinsically linked to broader technological trends.
The rise of cloud computing, for instance, has enabled greater accessibility and scalability, allowing businesses of all sizes to leverage the power of APS without significant upfront investment in hardware and infrastructure. Similarly, advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) have opened new avenues for optimization and predictive analytics within APS systems.
Impact of Cloud Computing on APS Calendar Accessibility and Scalability
Cloud-based APS calendars offer unparalleled accessibility, allowing users to access and manage schedules from any location with an internet connection. This eliminates the limitations of on-premise systems, which require dedicated hardware and software installations. Furthermore, cloud platforms offer scalability, enabling businesses to easily adjust their computing resources to meet fluctuating demands. For example, a manufacturing company experiencing seasonal peaks in production can seamlessly scale its APS calendar resources in the cloud to handle the increased workload without investing in additional hardware.
This flexibility translates to cost savings and improved resource utilization.
Integration of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in APS Calendars
The integration of AI and ML has significantly enhanced the predictive capabilities of APS calendars. These technologies enable the systems to analyze historical data, identify patterns, and forecast future demands with greater accuracy. This allows for proactive scheduling adjustments, reducing the risk of delays and improving overall efficiency. For instance, an AI-powered APS calendar can predict potential bottlenecks in a production line based on historical data and adjust the schedule accordingly, minimizing downtime and maximizing output.
Furthermore, ML algorithms can learn from user interactions and adapt the calendar’s functionality to better suit individual needs.
Enhanced User Experience through Intuitive Interfaces and Visualization Tools
Modern APS calendars prioritize user experience through intuitive interfaces and advanced visualization tools. Drag-and-drop functionality, interactive Gantt charts, and real-time data updates provide users with a clear and comprehensive view of their schedules. These features simplify complex scheduling tasks, making them more accessible to users with varying levels of technical expertise. For example, a user-friendly interface can significantly reduce the learning curve associated with adopting a new APS system, accelerating the time to value.
Interactive Gantt charts allow users to easily identify and resolve scheduling conflicts, while real-time data updates ensure that the calendar always reflects the most current information.
Future Developments in APS Calendar Technology
Future developments in APS calendar technology are likely to focus on further integration of AI and ML, improved interoperability with other systems, and enhanced personalization capabilities. We can anticipate more sophisticated predictive models that account for a wider range of variables, such as external factors like weather conditions or supply chain disruptions. Furthermore, increased integration with other enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems will enable seamless data flow and reduce manual data entry.
Personalized dashboards and customizable views will provide users with tailored information relevant to their specific roles and responsibilities. For example, a future APS calendar might incorporate real-time traffic data to optimize delivery schedules or use predictive maintenance algorithms to schedule equipment servicing proactively.
Data Management and Security in APS Calendars
The secure management of data within Advanced Planning and Scheduling (APS) calendar systems is paramount. A robust security framework is not merely a technical requirement; it is fundamental to maintaining user trust, protecting organizational reputation, and ensuring compliance with relevant data privacy regulations. Failure to adequately secure APS calendar data can lead to significant legal and financial repercussions, severely impacting the organization’s operational efficiency and long-term viability.
Importance of Secure Data Management
Secure data management in APS calendar systems is critical for several reasons. Data breaches can erode user trust, leading to decreased adoption and utilization of the system. This loss of confidence can extend beyond individual users to impact the organization’s overall reputation, potentially damaging its relationships with clients and partners. Furthermore, non-compliance with data privacy regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States can result in substantial fines, legal action, and reputational damage.
The financial ramifications of data breaches can be significant, encompassing costs associated with incident response, legal fees, regulatory penalties, and potential loss of revenue.
Potential Risks Associated with Insecure Data Storage and Handling
Insecure data storage and handling practices within an APS calendar system expose the organization to a multitude of risks. These risks can be broadly categorized and mitigated through proactive measures.
| Risk Category | Specific Risk | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Unauthorized Access | Data breaches via phishing or malware | Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA), robust access controls (RBAC), and employee security awareness training. Regularly update security software and conduct penetration testing. |
| Data Loss/Corruption | Hardware failure, accidental deletion | Regular backups (using the 3-2-1 rule: 3 copies, 2 different media, 1 offsite), data redundancy, and version control. Implement disaster recovery planning. |
| Insider Threats | Malicious or negligent employees | Implement strict access control based on the principle of least privilege, regular employee security training, and background checks. Monitor user activity for suspicious patterns. |
| Data Leaks | Improper configuration, vulnerabilities | Regular security audits, penetration testing, and prompt patching of vulnerabilities. Secure configuration management practices. |
| Privacy Violations | Exposure of sensitive personal information | Strict data anonymization/pseudonymization policies, data minimization, and adherence to relevant data privacy regulations. Implement data loss prevention (DLP) measures. |
Recommendations for Ensuring Data Security and Privacy
Implementing robust security measures is crucial for safeguarding user data within an APS calendar. This requires a multi-layered approach encompassing various technical and procedural controls.
Authentication and Authorization: Employ strong authentication methods such as OAuth 2.0 or OpenID Connect, coupled with multi-factor authentication (MFA). Implement role-based access control (RBAC) or attribute-based access control (ABAC) to restrict access to sensitive data based on user roles and attributes. Regularly review and update access permissions.
Data Encryption: Utilize Advanced Encryption Standard (AES)-256 encryption for both data at rest and data in transit. Implement key management systems to securely generate, store, and rotate encryption keys. Consider using hardware security modules (HSMs) for enhanced key protection.
Data Backup and Recovery: Establish a comprehensive backup and recovery strategy encompassing regular backups (daily or more frequent, depending on criticality), offsite storage, and a well-defined disaster recovery plan. Implement version control to allow for data restoration to previous states. Regularly test the backup and recovery process to ensure its effectiveness.
Security Auditing and Monitoring: Conduct regular security audits to identify and address vulnerabilities. Implement intrusion detection systems (IDS) and intrusion prevention systems (IPS) to monitor network traffic for malicious activity. Utilize Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems to collect, analyze, and correlate security logs from various sources. This enables proactive threat detection and response.
Compliance with Regulations: Ensure compliance with relevant data privacy regulations such as GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA (if applicable), and others. Document data processing activities, implement data subject access requests (DSAR) procedures, and maintain a record of processing activities (RPA).
Best Practices for Securing an APS Calendar System
- Implement multi-factor authentication for all users.
- Utilize strong encryption for data at rest and in transit.
- Conduct regular security audits and penetration testing.
- Establish a robust backup and recovery plan.
- Implement role-based access control.
- Enforce strong password policies and employee security awareness training.
- Maintain up-to-date security software and patches.
- Comply with all relevant data privacy regulations.
Hypothetical Data Breach Scenario and Incident Response
Imagine a scenario where a phishing email compromises an employee’s credentials, granting unauthorized access to the APS calendar system. The attacker gains access to sensitive scheduling data, including project timelines, resource allocations, and potentially confidential client information.The incident response plan would involve the following steps:
1. Containment
Immediately isolate the compromised account and system to prevent further data exfiltration.
2. Eradication
Remove the malware or exploit that enabled the breach.
3. Recovery
Restore the system from a clean backup.
4. Investigation
Conduct a thorough forensic investigation to determine the extent of the breach and identify the root cause.
5. Notification
Notify affected users and relevant authorities (depending on the nature of the data and applicable regulations).
6. Remediation
Implement corrective measures to prevent similar incidents in the future.
7. Post-Incident Review
Conduct a post-incident review to assess the effectiveness of the response plan and identify areas for improvement.
Ethical Considerations in Data Management and Security
Ethical considerations are central to data management and security in APS calendar systems. User privacy must be paramount. Data transparency is crucial, meaning users should be informed about how their data is collected, used, and protected. Organizations must prioritize data minimization, collecting only the data necessary for the system’s functionality. Transparency builds trust, while breaches erode it, potentially leading to legal ramifications and reputational damage.
A commitment to ethical data handling practices is essential for building and maintaining user trust and fostering a positive organizational reputation.
APS Calendar and its Role in Emergency Preparedness
The Advanced Planning System (APS) calendar, when properly implemented, becomes a crucial tool for effective emergency preparedness. Its ability to manage complex scheduling, integrate various data streams, and provide readily accessible information significantly enhances an organization’s capacity to respond to unforeseen events. By centralizing critical information and facilitating coordinated action, the APS calendar contributes to a more resilient and responsive emergency response system.The APS calendar facilitates emergency preparedness planning by providing a centralized platform for scheduling, tracking, and managing all aspects of emergency response.
This includes the planning and execution of drills, the dissemination of critical information to relevant personnel, and the coordination of resources during an actual emergency. Its ability to integrate with other systems allows for a holistic view of preparedness efforts.
Scheduling Drills and Exercises
Effective emergency preparedness requires regular drills and exercises to test response plans and identify weaknesses. The APS calendar allows for the efficient scheduling of these activities, including specifying dates, times, locations, participants, and specific objectives for each drill. For instance, a hospital might use the calendar to schedule fire drills, active shooter drills, and pandemic response simulations, ensuring that staff are adequately trained and prepared.
The calendar can also track attendance, record feedback, and identify areas needing improvement, all contributing to continuous improvement of emergency preparedness.
Dissemination of Critical Information
Timely dissemination of information is paramount during an emergency. The APS calendar can be used to disseminate critical information to relevant personnel, such as emergency contact details, evacuation routes, assembly points, and specific instructions during various emergency scenarios. For example, a university could use the calendar to broadcast weather alerts, campus closures, and instructions regarding shelter-in-place procedures. Alerts and notifications can be integrated directly into the calendar, ensuring that crucial information reaches the right people at the right time.
Accuracy and Accessibility in Emergency Preparedness Calendars
Accuracy and accessibility are fundamental to the success of any emergency preparedness plan. Inaccurate information or inaccessible calendars can lead to confusion, delays, and potentially catastrophic consequences. The APS calendar’s ability to ensure data integrity through version control and user permissions is vital. For example, a manufacturing facility utilizing the APS calendar for emergency shutdowns must ensure that the calendar’s information regarding emergency procedures is consistently updated and accessible to all relevant personnel, including contractors and temporary workers.
Real-time updates and clear communication protocols, facilitated by the APS calendar, are crucial for maintaining situational awareness and ensuring a coordinated response.
The Future of APS Calendars
APS calendars are evolving rapidly, driven by advancements in technology and changing user needs. The following analysis explores potential future trends, emerging technologies, and ethical considerations related to the development and application of APS calendars. This examination will also highlight the need for future research to address emerging challenges and opportunities in this dynamic field.
Potential Future Trends in APS Calendar Design and Functionality
Future APS calendars will likely be characterized by significant improvements in user interface/user experience, enhanced integration capabilities, and sophisticated data visualization and analytics.
User Interface/User Experience (UI/UX) Advancements
Advancements in UI/UX will focus on intuitive navigation, personalized views, and enhanced accessibility. We can expect to see customizable dashboards allowing users to prioritize tasks based on individual needs and preferences. AI-driven prioritization will intelligently arrange tasks based on deadlines, importance, and dependencies. Accessibility features will cater to diverse user needs, including those with visual, auditory, or motor impairments.
Innovative UI/UX patterns, such as natural language processing for task input and gesture-based controls, will enhance usability. For example, imagine a calendar that understands voice commands to schedule appointments or a calendar that adapts its layout to different screen sizes and devices seamlessly.
Integration with Other Systems
Seamless integration with project management software (like Asana or Trello), CRM systems (like Salesforce or HubSpot), email clients (like Outlook or Gmail), and other relevant applications will be crucial. This integration will automate data transfer, reducing manual input and the risk of errors. Quantifiable benefits include increased efficiency (estimated time savings of 15-20% in task management), improved collaboration, and reduced scheduling conflicts.
For instance, imagine a calendar that automatically pulls deadlines from a project management tool and flags potential conflicts with existing appointments.
Data Visualization and Analytics
Future APS calendars will leverage advanced data visualization techniques to provide insightful summaries and trends. Visualizations like Gantt charts will offer a clear overview of project timelines, while heatmaps will highlight periods of high workload or potential scheduling conflicts. Interactive dashboards will allow users to drill down into specific data points, gaining a deeper understanding of their scheduling patterns and identifying areas for improvement.
For example, a heatmap could visually represent the user’s daily workload, immediately identifying days with an excessive number of tasks.
Emerging Technologies Impacting APS Calendar Development
Several emerging technologies are poised to revolutionize APS calendars.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI will play a significant role in intelligent scheduling, automatically resolving conflicts and optimizing task allocation. AI-powered automated reminders will ensure timely completion of tasks, and predictive analytics will forecast potential scheduling bottlenecks. For instance, an AI could analyze past scheduling patterns to predict future workload and proactively suggest adjustments.
Extended Reality (XR) Technologies (VR/AR/MR)
XR technologies offer immersive scheduling and visualization capabilities. VR could provide a 3D representation of schedules, allowing users to “walk through” their day or week. AR could overlay schedule information onto the real world, providing contextual reminders and information. MR could combine both VR and AR elements for a more integrated experience. Imagine an AR application that overlays your schedule onto your physical workspace, highlighting upcoming deadlines and meetings in real-time.
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology can enhance security, transparency, and data integrity in shared APS calendars. By creating a secure and immutable record of scheduling information, blockchain can prevent unauthorized access and modifications. This is particularly valuable for collaborative projects or organizations that require high levels of data security. A blockchain-based system could guarantee the authenticity and integrity of scheduling data, preventing manipulation or fraud.
Predictions for the Evolution of APS Calendars
The following table presents predictions for the evolution of APS calendars over the next 3, 5, and 10 years.
| Timeframe | Predicted Feature/Functionality | Justification/Supporting Evidence | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 Years | Widespread adoption of AI-powered scheduling assistants | Current rapid advancements in AI and increasing demand for automation in task management. | Significant increase in scheduling efficiency and reduced human error. |
| 5 Years | Integration of AR/MR technology for contextual scheduling reminders and visualization. | Growing adoption of AR/MR technologies in various sectors and the potential for enhanced user engagement. | Improved user experience and enhanced understanding of scheduling data. |
| 10 Years | Ubiquitous use of blockchain for secure and transparent shared calendars, especially in sensitive industries. | Increasing concerns about data security and privacy, coupled with the growing maturity of blockchain technology. | Enhanced data security and trust in shared scheduling systems. |
Comparative Analysis of Existing APS Calendar Systems
The following table compares three existing APS calendar systems: Google Calendar, Microsoft Outlook Calendar, and Apple Calendar.
| Feature | Google Calendar | Microsoft Outlook Calendar | Apple Calendar |
|---|---|---|---|
| UI/UX | Intuitive and user-friendly, but lacks advanced customization options for some users. | Powerful but can be overwhelming for less tech-savvy users. Strong integration with Microsoft ecosystem. | Clean and simple interface, tightly integrated with Apple devices. |
| Integrations | Excellent integration with Google Workspace apps and many third-party tools. | Strong integration within the Microsoft ecosystem, but integration with other systems can be less seamless. | Good integration with Apple devices and apps, but integration with third-party tools can be limited. |
| Data Visualization | Basic visualization capabilities, primarily through calendar views. | Offers more advanced visualization options, particularly within the context of Microsoft Office applications. | Limited data visualization capabilities compared to Google Calendar and Microsoft Outlook Calendar. |
| Security | Robust security measures, leveraging Google’s infrastructure. | Strong security measures, benefiting from Microsoft’s extensive security expertise. | Solid security features, integrated with Apple’s overall security framework. |
Ethical Implications of Future APS Calendar Designs
Several ethical implications need to be considered regarding future APS calendar designs and functionalities.
- Data privacy concerns related to the collection and use of scheduling data.
- Algorithmic bias in AI-powered scheduling systems, potentially leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes.
- The potential for over-scheduling and burnout due to increased efficiency and automation.
- Accessibility issues if not designed inclusively for diverse user needs.
Future Research Directions
Further research is needed to address several critical gaps in our understanding of the future of APS calendars.
- Investigate the impact of AI-driven scheduling on employee well-being and work-life balance.
- Develop ethical guidelines for the design and implementation of AI-powered scheduling systems to mitigate bias and ensure fairness.
- Explore the potential of XR technologies to enhance collaboration and communication in shared scheduling environments.
Case Studies of Effective APS Calendar Use
This section presents a hypothetical case study illustrating the practical application and benefits of Advanced Planning and Scheduling (APS) calendars in optimizing operational efficiency. The example focuses on a manufacturing environment, highlighting the positive impact on resource allocation and production scheduling.
Effective APS calendar implementation requires careful consideration of various factors, including system integration, data accuracy, and user training. The successful deployment demonstrated below underscores the importance of a holistic approach to APS calendar integration within an organization.
Hypothetical Case Study: Optimized Production Scheduling in a Manufacturing Plant
This case study examines “Acme Manufacturing,” a company producing specialized electronic components. Prior to implementing an APS calendar, Acme experienced frequent production delays, resource bottlenecks, and suboptimal inventory management. Their traditional scheduling system lacked the real-time visibility and predictive capabilities offered by an APS solution. The implementation of an APS calendar provided a centralized platform for managing all aspects of the production process, including machine scheduling, material requirements planning (MRP), and workforce allocation.
The system integrated seamlessly with existing Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software, allowing for a smooth data transfer and minimizing manual data entry.
The APS calendar allowed Acme to visualize the entire production process, identify potential bottlenecks in advance, and proactively adjust schedules to mitigate delays. For instance, the system accurately predicted material shortages based on current production plans and automatically generated purchase orders to ensure timely delivery. Furthermore, the APS calendar optimized machine utilization by assigning tasks based on machine capabilities and availability, minimizing idle time and maximizing throughput.
The system also factored in employee skills and availability, leading to efficient workforce allocation and reduced overtime costs.
Benefits and Outcomes of APS Calendar Implementation at Acme Manufacturing
The implementation of the APS calendar resulted in several significant improvements across various operational aspects of Acme Manufacturing. Production lead times were reduced by 15%, significantly improving customer satisfaction and order fulfillment rates. Inventory levels were optimized, reducing storage costs and minimizing the risk of obsolescence. Machine utilization increased by 10%, resulting in higher production output and increased profitability.
Finally, workforce scheduling efficiency improved, leading to a 5% reduction in overtime costs. These quantifiable results demonstrate the significant return on investment (ROI) associated with implementing an APS calendar.
These improvements were not only quantitative but also qualitative. The enhanced visibility and predictive capabilities of the APS calendar empowered managers to make more informed decisions, leading to a more proactive and responsive approach to production management. The improved coordination and communication fostered a more collaborative work environment, further contributing to overall efficiency and organizational effectiveness.
Improved Efficiency and Organization Through APS Calendar Use
The APS calendar at Acme Manufacturing facilitated a shift from reactive to proactive production management. The ability to anticipate and address potential issues before they escalated minimized disruptions and ensured a smoother workflow. The centralized platform streamlined communication and information sharing among different departments, eliminating data silos and fostering better collaboration. This improved organizational efficiency and facilitated faster decision-making.
The system’s user-friendly interface and intuitive design ensured easy adoption by employees, minimizing training time and maximizing user acceptance. The improved transparency and accountability fostered by the system enhanced overall operational control and performance.
Common Misconceptions about APS Calendars
Advanced Planning and Scheduling (APS) calendars are powerful tools for optimizing resource allocation and streamlining operations. However, several misconceptions surrounding their functionality and capabilities often hinder their effective implementation. Understanding these misconceptions is crucial for maximizing the benefits of APS systems.
Common Misconceptions Regarding APS Calendars
The following points address frequently held, but inaccurate, beliefs about APS calendars. These misconceptions often stem from a lack of understanding of the underlying technology and its broader applications.
- Misconception: APS calendars are overly complex and difficult to use. Reality: While APS systems can be sophisticated, many modern systems offer user-friendly interfaces and intuitive navigation. The complexity is often in the underlying algorithms optimizing schedules, not in the user experience. Proper training and clear documentation can mitigate any perceived difficulty.
- Misconception: APS calendars only work with perfectly accurate data. Reality: APS calendars are designed to handle uncertainty and variability in data. Robust systems incorporate forecasting and what-if analysis to accommodate changes and inaccuracies in input data. The value lies in the ability to adapt and re-optimize schedules in response to real-world variations.
- Misconception: Integration with existing systems is always difficult and time-consuming. Reality: Many modern APS systems offer seamless integration with ERP and other enterprise software through APIs and standard data exchange formats. While some integration projects may be complex, the potential benefits often outweigh the initial effort. Careful planning and selection of compatible systems can minimize integration challenges.
- Misconception: APS calendars are inflexible and cannot adapt to changing demands. Reality: Effective APS systems incorporate dynamic scheduling capabilities, allowing for adjustments based on real-time changes in demand, resource availability, or unexpected events. Rescheduling algorithms automatically find optimal solutions within the constraints of the updated data.
- Misconception: APS calendars are only suitable for large organizations with extensive resources. Reality: While larger organizations may benefit from more comprehensive features, APS systems are scalable and can be adapted to suit businesses of various sizes. Cloud-based solutions further reduce the barrier to entry, offering flexible pricing and accessibility.
Comparison of Misconceptions Regarding Data Synchronization
| Misconception | Reality | Supporting Evidence |
|---|---|---|
| APS calendars only update data once per day, leading to scheduling inaccuracies. | Many modern APS calendars offer real-time or near real-time data synchronization, ensuring schedules reflect the most current information. The frequency of updates depends on system configuration and integration capabilities. | Documentation from leading APS vendors typically specifies update frequency and data synchronization mechanisms (e.g., API specifications, database connection details). |
| Real-time data updates in APS calendars are too resource-intensive and slow down the system. | Efficiently designed APS systems leverage optimized algorithms and database technologies to handle real-time updates with minimal performance impact. The impact depends on the system’s architecture and the volume of data. | Performance benchmarks and case studies from APS vendors often demonstrate the efficiency of real-time data handling. |
APS Calendar Applications Beyond Production Scheduling
APS calendars are not limited to production scheduling. Their capabilities extend to various operational areas, offering significant benefits in planning and resource optimization.
- Maintenance Scheduling: Optimizing maintenance tasks to minimize downtime and maximize equipment lifespan.
- Resource Allocation: Efficiently assigning personnel, equipment, and materials across different projects or tasks.
- Project Management: Tracking project progress, identifying potential bottlenecks, and managing dependencies.
- Supply Chain Management: Coordinating material flows, managing inventory levels, and optimizing transportation schedules.
- Human Resource Management: Scheduling employees based on skill sets, availability, and project requirements.
Core Functionality of an APS Calendar
APS calendars go beyond basic scheduling by incorporating sophisticated algorithms to optimize resource allocation and minimize conflicts. These systems typically include features such as constraint management (e.g., resource availability, deadlines, precedence relationships), what-if analysis, and scenario planning. Underlying algorithms, such as constraint programming or linear programming, are used to find optimal schedules that satisfy all defined constraints. These algorithms consider various factors to create efficient and feasible plans.
Visual Comparison: APS vs. Traditional Calendar
APS Calendar | Traditional Calendar
——————————————–|————————–
Optimized scheduling based on constraints | Basic scheduling, limited constraint handlingReal-time data updates and dynamic rescheduling | Static scheduling, infrequent updatesWhat-if analysis and scenario planning | Limited scenario planning capabilitiesResource allocation and optimization | Limited resource allocation featuresIntegration with other systems | Limited or no integration
Simple APS Scheduling Algorithm (Pseudocode)
“`function optimizeSchedule(tasks, resources, constraints) // Initialize schedule schedule = emptySchedule; // Iterate through tasks for each task in tasks // Find best available resource bestResource = findBestResource(task, resources, schedule, constraints); // Assign task to resource if (bestResource != null) schedule.addTask(task, bestResource); else // Handle task conflicts (e.g., reschedule, flag as infeasible) return schedule;function findBestResource(task, resources, schedule, constraints) // Evaluate resource availability and constraints // …
(complex logic to evaluate resource suitability and constraint satisfaction) … return bestResource;“`This pseudocode demonstrates a simplified approach to scheduling. The `optimizeSchedule` function iterates through tasks, attempting to assign each task to the most suitable resource based on availability and constraints. The `findBestResource` function encapsulates the complex logic of evaluating resource suitability and constraint satisfaction. More sophisticated algorithms would employ techniques like constraint propagation or heuristic search to handle complex scheduling problems efficiently.
Frequently Asked Questions about APS Calendars
- Q: How do I set up an APS calendar? A: Setup involves defining resources, tasks, constraints, and integrating with existing systems. Consult vendor documentation for specific steps.
- Q: How do I use an APS calendar for capacity planning? A: APS calendars allow you to model capacity needs, forecast future demand, and identify potential bottlenecks by simulating different scenarios.
- Q: What happens if a task is delayed? A: The system will automatically attempt to reschedule the task, considering resource availability and constraints. Users may need to manually intervene in some cases.
- Q: How do I integrate my APS calendar with my ERP system? A: Integration methods vary depending on the systems involved, but common approaches include APIs and data exchange formats (e.g., XML, CSV).
- Q: What are the key performance indicators (KPIs) for an APS calendar? A: KPIs can include on-time delivery rates, resource utilization, and overall production efficiency.
- Q: Can I customize the reports generated by the APS calendar? A: Most APS systems offer customizable reporting features, allowing users to tailor reports to their specific needs.
- Q: How secure is the data stored in an APS calendar? A: Security measures vary depending on the vendor, but generally include encryption, access controls, and regular security audits.
- Q: What type of training is required to use an APS calendar? A: Training needs depend on system complexity and user roles, ranging from basic tutorials to comprehensive workshops.
- Q: What if my APS calendar encounters an error? A: Most systems include error logging and troubleshooting tools. Vendor support can also assist with resolving issues.
- Q: What is the cost of implementing an APS calendar? A: Costs vary depending on the vendor, system features, and implementation complexity. Consider both software licensing and implementation services.
FAQs in Table Format
| Question | Answer | s |
|---|---|---|
| How do I set up an APS calendar? | Setup involves defining resources, tasks, constraints, and integrating with existing systems. Consult vendor documentation for specific steps. | Setup, Configuration, Installation |
| How do I use an APS calendar for capacity planning? | APS calendars allow you to model capacity needs, forecast future demand, and identify potential bottlenecks by simulating different scenarios. | Capacity Planning, Forecasting, Simulation |
| What happens if a task is delayed? | The system will automatically attempt to reschedule the task, considering resource availability and constraints. Users may need to manually intervene in some cases. | Task Delay, Rescheduling, Constraints |
| How do I integrate my APS calendar with my ERP system? | Integration methods vary depending on the systems involved, but common approaches include APIs and data exchange formats (e.g., XML, CSV). | Integration, ERP, API, Data Exchange |
| What are the key performance indicators (KPIs) for an APS calendar? | KPIs can include on-time delivery rates, resource utilization, and overall production efficiency. | KPI, On-Time Delivery, Resource Utilization, Efficiency |
| Can I customize the reports generated by the APS calendar? | Most APS systems offer customizable reporting features, allowing users to tailor reports to their specific needs. | Reporting, Customization, Report Generation |
| How secure is the data stored in an APS calendar? | Security measures vary depending on the vendor, but generally include encryption, access controls, and regular security audits. | Security, Data Security, Encryption, Access Control |
| What type of training is required to use an APS calendar? | Training needs depend on system complexity and user roles, ranging from basic tutorials to comprehensive workshops. | Training, User Training, System Training |
| What if my APS calendar encounters an error? | Most systems include error logging and troubleshooting tools. Vendor support can also assist with resolving issues. | Error Handling, Troubleshooting, Support |
| What is the cost of implementing an APS calendar? | Costs vary depending on the vendor, system features, and implementation complexity. Consider both software licensing and implementation services. | Cost, Implementation Cost, Licensing, Services |
FAQ: Aps Calendar 2024 2025
Q: What does “APS” stand for in the context of the APS Calendar?
A: The specific meaning of “APS” depends on the institution or organization using the calendar. It often refers to a particular system or department (e.g., Academic Planning System).
Q: How can I access the APS Calendar if I am a student?
A: Access is typically provided through the institution’s official website, student portal, or learning management system (LMS). Check your school’s communication channels for specific instructions.
Q: What happens if there is a conflict between events scheduled on the APS Calendar?
A: The resolution of scheduling conflicts depends on the nature of the events and institutional policies. It may require communication with relevant parties to find a suitable alternative time or arrangement.
Q: Can the APS Calendar be customized to reflect personal preferences?
A: Customization options vary depending on the platform. Some calendars allow for personalized views, reminders, and color-coding, while others may offer limited flexibility.
Q: What security measures are in place to protect the data on the APS Calendar?
A: Security measures typically include data encryption, access controls, regular backups, and compliance with relevant data privacy regulations. Specific details vary depending on the system and institution.